Biden moves to protect the Tongass, North America's largest rainforest, from logging and road building
- Written by Beverly Law, Professor Emeritus of Global Change Biology and Terrestrial Systems Science, Oregon State University
Ask people to find the world’s rainforests on a globe, and most will probably point to South America. But North America has rainforests too – and like their tropical counterparts, these temperate rainforests[1] are ecological treasures.
The Biden administration recently announced new policies[2] to protect the Tongass National Forest[3], the largest intact temperate rainforest in the world and the biggest U.S. national forest. It spreads over more than 26,000 square miles (67,340 square kilometers) – roughly the size of West Virginia – and covers most of southeast Alaska. The Tongass has thousands of watersheds and fjords, and more than a thousand forested islands.
 Alaska’s national forests, the Chugach and the Tongass, compared with the lower 48 states.
USFS[4]
Alaska’s national forests, the Chugach and the Tongass, compared with the lower 48 states.
USFS[4]
For over 20 years the Tongass has been at the center of political battles over two key conservation issues: old-growth logging[5] and designating large forest zones as roadless areas[6] to prevent development. As a scientist specializing in forest ecosystems[7], I see protecting the Tongass as the kind of bold action that’s needed to address climate change and biodiversity loss[8].
An ecological gem
The Tongass as we know it today began forming at the end of the Little Ice Age[9] in the mid-1700s, which left much of what is now southern Alaska as barren land. Gradually, the area repopulated with plants and animals to become a swath of diverse, rich old-growth forests. President Theodore Roosevelt designated the Tongass as a forest reserve in 1902, and then as a national forest in 1907.
The Tongass is the traditional homeland[10] of the Tlingit, Haida and Tsimshian people. It is named for the Tongass group of the Tlingit people, who have continuously occupied the area for over 10,000 years[11]. Alaska Natives relied on the forest’s rich diversity of plants and animals for their survival and traditions. Today the Tongass has abundant populations of animals that have become uncommon in other parts of the U.S., such as brown bears and wolves.
Most of the 900 watersheds[12] within the Tongass are in near-natural condition. This ensures that they can provide habitat for many wild species and recover from or adapt to stresses, such as warmer temperatures due to climate change. They support salmon that spawn in the forest’s creeks and rivers, providing food for bears, eagles and other predators[13]. Such ecosystems are incredibly rare around the world today.
The Tongass National Forest is home to bears, bald eagles and five species of salmon.How roads threaten forests
Intact old-growth forests, with trees hundreds of years old, are essential for carbon storage, biodiversity and climate resilience. They have fully developed root systems that can reach water in deep soils, and are more resistant than young forests to drought, fire, insects and strong winds – effects that are all likely to increase with climate change[14].
Because old-growth forests have accumulated massive amounts of carbon in their trees and soils over centuries, protecting them is an important strategy for curbing climate change[15]. Today, however, scientists estimate that logging, agriculture and urban development have left only 6%[16] to 14%[17] of the forest area in the U.S. intact. And only 7% of total U.S. forest area[18] is more than a century old.
Old-growth logging is controversial[19] because intact forests are so rare. And forest losses often start when roads are cut through them to access timber. The roads are effectively long clear-cuts across the landscape.
Building roads through moist temperate forests can make it easier for warm air, wind and sunlight to penetrate from the edges to the interior, drying soil, mosses and ferns. It also provides entry points for invasive plants carried in by vehicles.
And roads’ negative effects extend beyond the actual driving surface. A road 30 feet (9 meters) wide may influence an additional 80 to 100 feet (25 to 30 meters) of adjacent land because of land disturbance during construction and wide buffer zones created for vehicle safety.
Road building can harm animals like brown bears[20] through collisions with vehicles and increased poaching and trapping. In the Tongass, a strip a quarter-mile (0.4 kilometer) wide on each side of the highway system is closed to big game hunting[21], but this can mitigate only some of roads’ pervasive effects.
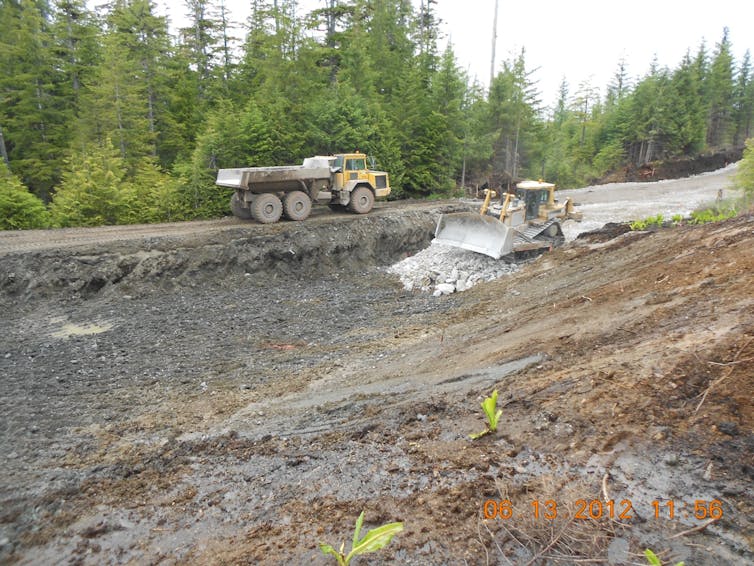 Upgrading a logging road into State Highway 43 on Prince of Wales Island in the Tongass National Forest.
Jack Olen, USFS Alaska Region/Flickr, CC BY[22][23]
Upgrading a logging road into State Highway 43 on Prince of Wales Island in the Tongass National Forest.
Jack Olen, USFS Alaska Region/Flickr, CC BY[22][23]
Decades of controversy
In its final days in January 2001, the Clinton administration adopted the Roadless Area Conservation Rule[24], which barred logging, timber sales, mining and road construction within inventoried roadless areas in most national forests across the U.S. About 9.2 million acres (37,231 square kilometers) of the Tongass – more than half of its area – were designated and managed as inventoried roadless areas.
This step launched 20 years of debate and litigation[25]. The Bush and Trump administrations, supported by conservative Western state officials, sought to limit the roadless rule and exempt the Tongass from it. The Obama administration generally supported the rule and defended it in court.
In 2020, the Trump administration opened the Tongass to extensive new logging, mining and road construction activities[26]. Critics, including environmental advocates and tribal governments, argued that Alaska’s economy was better served by outdoor recreation and commercial fishing[27] than by clear-cutting its remaining old-growth forests.
Now the Biden administration has restored protection for roadless areas of the Tongass. It also has pledged to end large-scale old-growth timber sales[28] and focus on restoration, recreation and other noncommercial activities. It will permit old-growth logging only for cultural uses, such as totem poles and canoes, and for small sales that serve community needs. It also proposes a US$25 million investment in sustainable economic opportunities, with particular focus on investments that are responsive to Indigenous needs.
Forest advocates have welcomed this action and the administration’s plan to publish a new version of the roadless rule[29]. But it remains to be seen how permanent this shift will be.
A strategic climate reserve
New hope for protecting the Tongass comes amid growing alarm over two converging environmental crises: climate change and accelerated extinctions of plant and animal species. In my view, protecting ecological treasures like the Tongass is a critical way to address both issues at once, as scientists have recommended[30].
The southeastern and south-central regions of Alaska, which contain the Tongass and Chugach[31] national forests, store about 1 billion metric tons of carbon in live and dead tree biomass. This amount could increase by 27% by 2100[32] if the forest is allowed to continue to grow and accumulate carbon.
I believe the Tongass’ vast intactness, rich biodiversity and significant carbon storage make it an excellent choice as the first of a series of strategic climate reserves[33] – areas that scientists have proposed setting aside to protect large carbon sinks and biodiversity of plant and animal species. U.S. old-growth forests are disappearing rapidly, but with smart management they can deliver ecological benefits for decades to come.
[Like what you’ve read? Want more? Sign up for The Conversation’s daily newsletter[34].]
References
- ^ temperate rainforests (www.wilderness.org)
- ^ announced new policies (www.usda.gov)
- ^ Tongass National Forest (www.fs.usda.gov)
- ^ USFS (www.fs.fed.us)
- ^ old-growth logging (www.scientificamerican.com)
- ^ roadless areas (islandpress.org)
- ^ scientist specializing in forest ecosystems (scholar.google.com)
- ^ climate change and biodiversity loss (www.un.org)
- ^ Little Ice Age (theconversation.com)
- ^ traditional homeland (www.indianz.com)
- ^ over 10,000 years (www.fs.usda.gov)
- ^ 900 watersheds (www.fs.usda.gov)
- ^ providing food for bears, eagles and other predators (www.adfg.alaska.gov)
- ^ likely to increase with climate change (science2017.globalchange.gov)
- ^ an important strategy for curbing climate change (theconversation.com)
- ^ 6% (www.scientificamerican.com)
- ^ 14% (dx.doi.org)
- ^ 7% of total U.S. forest area (doi.org)
- ^ Old-growth logging is controversial (theconversation.com)
- ^ brown bears (www.sierraclub.org)
- ^ closed to big game hunting (www.adfg.alaska.gov)
- ^ Jack Olen, USFS Alaska Region/Flickr (flic.kr)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ Roadless Area Conservation Rule (www.fs.usda.gov)
- ^ 20 years of debate and litigation (eelp.law.harvard.edu)
- ^ extensive new logging, mining and road construction activities (www.reuters.com)
- ^ outdoor recreation and commercial fishing (insideclimatenews.org)
- ^ end large-scale old-growth timber sales (www.usda.gov)
- ^ publish a new version of the roadless rule (www.adn.com)
- ^ address both issues at once, as scientists have recommended (ipbes.net)
- ^ Chugach (www.fs.usda.gov)
- ^ 27% by 2100 (doi.org)
- ^ strategic climate reserves (wild-heritage.org)
- ^ Sign up for The Conversation’s daily newsletter (theconversation.com)
Authors: Beverly Law, Professor Emeritus of Global Change Biology and Terrestrial Systems Science, Oregon State University

