How gay neighborhoods used the traumas of HIV to help American cities fight coronavirus
- Written by Daniel Baldwin Hess, Professor of Urban and Regional Planning, University at Buffalo
Throughout the pandemic, local neighborhoods have played a critical and well-documented[1] role providing the health and social services necessary for American communities and businesses to survive and recover from the COVID-19 pandemic.
Gay neighborhoods were particularly well equipped[2] to meet this challenge, according to our latest research on these communities[3].
We find that the lessons learned and trauma experienced early in the HIV/AIDS pandemic[4] helped urban gay areas respond to COVID-19 quickly and effectively[5] – especially in the face of early federal government paralysis.
How gay neighborhoods fought HIV/AIDS
Gay neighborhoods are those that welcome lesbian, gay, bisexual, transsexual, queer and other sexual minorities[6] – a population generally referred to by the shorthand LGBTQ+. Well-known examples include the Castro district in San Francisco, Dupont Circle in Washington and Greenwich Village and Chelsea in New York City.
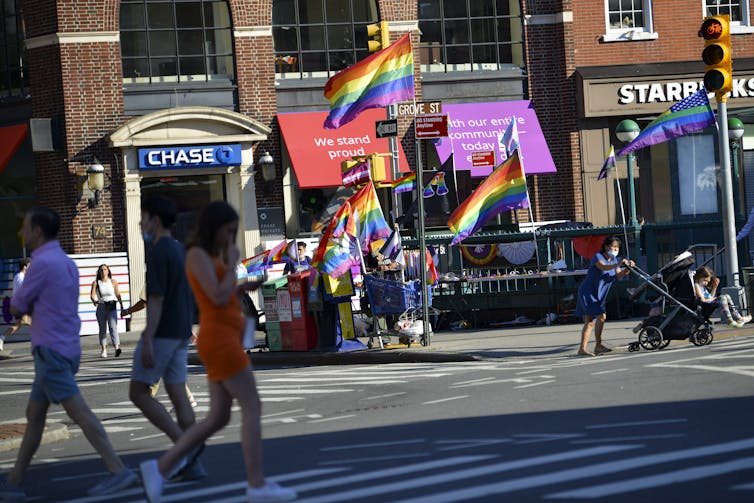 New York City’s West Village neighborhood during Pride month, June 2021.
Alexi Rosenfeld/Getty Images[7]
New York City’s West Village neighborhood during Pride month, June 2021.
Alexi Rosenfeld/Getty Images[7]
“Gayborhoods” grew during the sexual liberation movements of the 1960s and 1970s, offering LGTBQ people and their allies an escape from pervasive discrimination and prejudice[8]. In these areas, sexual minorities could rent apartments, socialize in bars and express themselves freely in a like-minded, compassionate community.
Even as LGBTQ people in the U.S. began to live more openly, gay neighborhoods really coalesced around the HIV/AIDS pandemic[9].
When that mysterious new disease began ravaging the LGBTQ community in the 1980s, the U.S. government turned away from, not toward, those communities. Support critical for fighting HIV – including health care subsidies for uninsured people and funding for research on treatments and cures[10] – was initially not provided[11]. Information given[12] by governments about disease transmission and treatment was inconsistent and sometimes inaccurate.
Government neglect ended up stigmatizing people with HIV and leading to many avoidable deaths. So, as we uncovered in our most recent book[13], gay neighborhoods filled the void where government and mainstream organizations failed. They became the battlefields where the AIDS pandemic was fought and eventually won.
People in gay neighborhoods developed community organizations and systems to deliver health care and mental health services, provide social support for LGBTQ+ people and support LGBTQ-friendly businesses.
Public health organizations like New York City’s Gay Men’s Health Crisis[14] also stepped in to do what many doctors would not. They shared information about slowing and stopping the spread of HIV and also distributed condoms, conducted free HIV testing and connected people who tested positive to help.
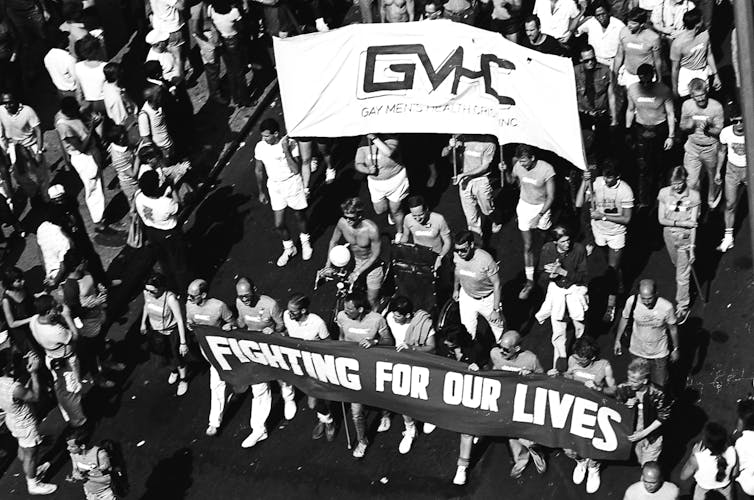 New York City’s Pride march in June 1985, featuring a contingent from the Gay Men’s Health Crisis.
Suzanne Poli/Getty Images[15]
New York City’s Pride march in June 1985, featuring a contingent from the Gay Men’s Health Crisis.
Suzanne Poli/Getty Images[15]
Building community through crisis
The COVID-19 pandemic shares many similarities[16] reminiscent of early days of the HIV/AIDS pandemic.
With both HIV/AIDS and COVID-19, there was a disjointed and bungled government response that endangered lives and produced both fear[17] and stigma[18]. Even some of the same government-appointed leaders were in place: Both Dr. Anthony Fauci[19] and Dr. Deborah Birx worked on marshaling government resources to spearhead the medical response to HIV in the 1990s.
With COVID-19, as with HIV/AIDS, city and state governments were unprepared to fight a disease outbreak[20]. They lacked both planning and infrastructure to effectively fight a rapidly accelerating public health threat.
Several U.S. states, as a result, looked to organizations within gay neighborhoods for help, relying on neighborhood-based LGBTQ+ health care organizations[21] to help support their COVID-19 pandemic response[22].
 Example of social distancing signage from Toronto gay neighborhood.
Robert Modzelewski, CC BY[23]
Example of social distancing signage from Toronto gay neighborhood.
Robert Modzelewski, CC BY[23]
For example, in New York, the Erie County Department of Health requested that Evergreen Health[24] – an LGBTQ community group originally established in the 1980s as a volunteer effort to fight HIV – assume responsibility for HIV testing during[25] the COVID-19 pandemic so that the county government could focus on COVID-19 testing. Evergreen also opened a drive-though COVID-19 testing center[26] in the spring of 2020 – four decades after it had introduced HIV testing to the Buffalo region.
Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, Evergreen Health not only continued to provide health care and other supportive services to Buffalo’s LGBTQ community but expanded offerings to better serve underserved and minority neighborhoods[27] across the city. At that time, New York state was the global epicenter[28] of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In Chicago and other cities, activists used LGBTQ+ urban social and professional networks[29] established during the HIV/AIDS pandemic[30] to tackle this latest disease. Queer communities disseminated information about COVID-19 to neighbors and distributed face masks and other protective gear[31], just as they had once shared information about HIV transmission and given out condoms.
[The Conversation’s most important coronavirus headlines, weekly in a science newsletter[32]]
Lessons learned
States with major grassroots activism in the HIV crisis also applied lessons from that era about overcoming misinformation[33] and fear of contagious diseases[34].
For instance, New York state used a network of small laboratories to process its COVID-19 tests and administer vaccines – a model pioneered during the emergence of the HIV/AIDS pandemic[35] when large, centralized laboratories were initially nervous about working with HIV-positive blood samples. Early on in the COVID-19 pandemic, this allowed New York to react effectively and process COVID-19 tests relatively quickly.
New York, followed by California, was among states in which COVID-19 infection first showed up in the U.S. As these state governments[36] set up testing procedures, they drew upon methods for testing established during the HIV/AIDS pandemic[37]. The experience in both New York and California with HIV/AIDS helped, at least in part, to establish robust testing networks during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The United Kingdom government[38], on the other hand, chose centralized laboratories to process tests, rejecting an offer to create a complementary network of smaller local providers. That decision may have complicated testing and slowed results[39] and contact tracing, according to reporting by SkyNews[40].
Our research also finds gay neighborhoods banded together to meet the needs of the broader community[41].
Activist mutual aid networks[42] formed decades ago within “gayborhoods” deployed peer-to-peer mobile technologies to help feed locked down and sick people[43] – not only within the LGBTQ community.
Many of these efforts to combat COVID-19[44], like actions taken to fight HIV/AIDS[45], were done quietly, without fanfare. This neighbor-helping-neighbor approach is a hallmark of the leadership[46] that can be found in gay neighborhoods – experienced rescuers[47] in times of crisis.
References
- ^ well-documented (link.springer.com)
- ^ Gay neighborhoods were particularly well equipped (www.thebody.com)
- ^ these communities (link.springer.com)
- ^ lessons learned and trauma experienced early in the HIV/AIDS pandemic (www.advocate.com)
- ^ urban gay areas respond to COVID-19 quickly and effectively (link.springer.com)
- ^ welcome lesbian, gay, bisexual, transsexual, queer and other sexual minorities (link.springer.com)
- ^ Alexi Rosenfeld/Getty Images (www.gettyimages.com)
- ^ pervasive discrimination and prejudice (link.springer.com)
- ^ coalesced around the HIV/AIDS pandemic (www.cdc.gov)
- ^ funding for research on treatments and cures (www.DOI.org)
- ^ was initially not provided (www.glsen.org)
- ^ Information given (www.nbcnews.com)
- ^ our most recent book (link.springer.com)
- ^ Gay Men’s Health Crisis (www.advocate.com)
- ^ Suzanne Poli/Getty Images (www.gettyimages.com)
- ^ shares many similarities (www.forbes.com)
- ^ disjointed and bungled government response that endangered lives and produced both fear (dailycampus.com)
- ^ stigma (abc11.com)
- ^ Dr. Anthony Fauci (www.axios.com)
- ^ city and state governments were unprepared to fight a disease outbreak (www.glsen.org)
- ^ neighborhood-based LGBTQ+ health care organizations (www.thebody.com)
- ^ COVID-19 pandemic response (link.springer.com)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ Evergreen Health (www.evergreenhs.org)
- ^ HIV testing during (www.advocate.com)
- ^ opened a drive-though COVID-19 testing center (www.evergreenhs.org)
- ^ underserved and minority neighborhoods (www.bu.edu)
- ^ New York state was the global epicenter (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ LGBTQ+ urban social and professional networks (time.com)
- ^ HIV/AIDS pandemic (www.advocate.com)
- ^ distributed face masks and other protective gear (www.ama-assn.org)
- ^ The Conversation’s most important coronavirus headlines, weekly in a science newsletter (theconversation.com)
- ^ overcoming misinformation (www.cdc.gov)
- ^ fear of contagious diseases (www.kqed.org)
- ^ a model pioneered during the emergence of the HIV/AIDS pandemic (www.hiv.gov)
- ^ these state governments (www.reuters.com)
- ^ they drew upon methods for testing established during the HIV/AIDS pandemic (goodmenproject.com)
- ^ United Kingdom government (www.bbc.com)
- ^ may have complicated testing and slowed results (www.bmj.com)
- ^ according to reporting by SkyNews (news.sky.com)
- ^ gay neighborhoods banded together to meet the needs of the broader community (link.springer.com)
- ^ mutual aid networks (www.kff.org)
- ^ help feed locked down and sick people (www.them.us)
- ^ Many of these efforts to combat COVID-19 (link.springer.com)
- ^ fight HIV/AIDS (www.kff.org)
- ^ hallmark of the leadership (www.fredhutch.org)
- ^ experienced rescuers (www.thedailybeast.com)
Authors: Daniel Baldwin Hess, Professor of Urban and Regional Planning, University at Buffalo

