Election violence in November? Here’s what the research says
- Written by Ore Koren, Assistant Professor, Indiana University Bloomington; International Security Fellow, Indiana University
After Kenya’s 2007 election, as incumbent President Mwai Kibaki declared victory, the opposition alleged the election had been rigged.
A wave of protests, riots and ethnic violence[1] followed. As many as 1,500 citizens were killed and another 600,000 forcibly displaced.
As the U.S. presidential election draws near, many have expressed concern that a similar scenario may unfold here[2]. Some envision President Donald Trump’s supporters using misinformation to mobilize vigilante militias[3] to clash with leftist protesters. Others envision that groups on the left will refuse to accept the results and mobilize[4], leading to violence and deaths across the country.
Having a contested election in times of crisis, however, is by no means a guarantee of violence. The front-runners in the 2017 French presidential election, for example, were as politically polarizing[5] as their U.S. 2020 counterparts, with centrist candidate Emmanuel Macron calling right-wing leader Marine Le Pen’s party racist and xenophobic[6] and Le Pen charging that Macron was “the candidate of savage globalisation[7].”
And the first round of voting in France took place just after a shooting in the heart of Paris sent the country into a state of emergency[8]. Yet, as the votes were counted and Macron was declared the winner, Le Pen conceded defeat[9], allowing for a peaceful transition.
With the barrage of 24/7 media coverage of the upcoming U.S. election, it can be hard to tell what’s real and what’s not – and that can be frightening. It’s important to step back and ask: What does the research say about the likelihood of election-related violence in November?
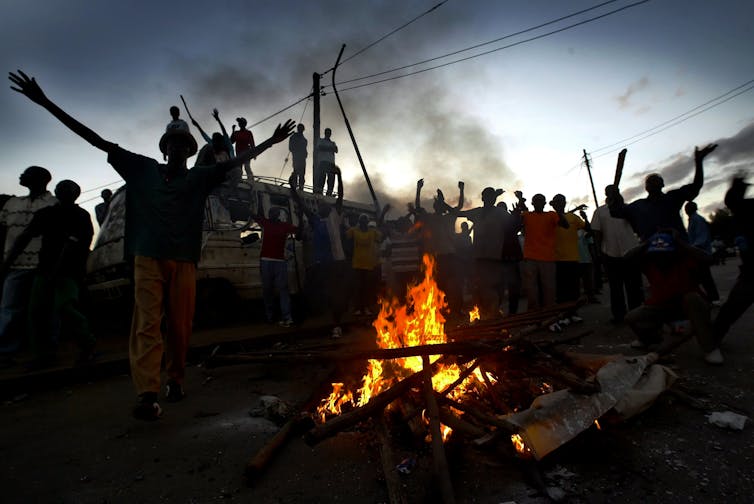 Deadly violence followed the disputed 2007 presidential election in Kenya, including in this Nairobi slum.
Tony Karumba/AFP/Getty Images[10]
Deadly violence followed the disputed 2007 presidential election in Kenya, including in this Nairobi slum.
Tony Karumba/AFP/Getty Images[10]
Predicting political instability
When social science researchers like me[11] try to predict political violence, we look at a large number of historical cases across multiple countries, and try to identify which events have resulted in many casualties.
In taking this approach, we can systematically evaluate what explains these extreme events, pinpointing specific issues that were present in most of the situations, and avoiding the inaccuracies that can happen by relying too much on anecdotal stories.
Such studies have highlighted three factors relevant to the upcoming election.
First, strong political institutions are especially effective[12] in reducing the risk of violence. Many have voiced concerns that President Trump has weakened American political institutions[13]. But as one of the world’s longest-enduring democracies, the United States and its democratic institutions have proven their capacity to maintain order through crises and abuse of presidential power[14] before.
In the U.S., for example, despite allegations to the contrary, electoral fraud is extremely rare[15]. Even if uncertainty and chaos were to ensue in the wake of the election, the authority to decide a winner is vested in an independent institution such as the U.S. Supreme Court[16] or by the House of Representatives[17]. Kenya in 2007 had no comparable institutional anchors to help ensure post-election stability.
Second, research, including my own[18], finds that mass political violence usually happens in countries that have no capacity to prevent it[19]. In Kenya, for example, most violence was perpetrated by unofficial militias affiliated with ethnic or religious groups, such as the Mungiki[20], which the government was unable – or unwilling – to curb.
In the U.S., if any political leader calls for vigilantes to mobilize, both the federal government and states have the capacity to expeditiously eliminate this threat. Militias may be armed, but they are no match for a well-trained National Guard[21] or Army regiment. This should help deter the risk of violence by vigilantes[22].
Some, however, fear that the president will send federal agencies to seize ballots[23]. Although military officers continue to express formal commitment[24] to keeping the military nonpoliticized[25], such actions, if taken, may result in a violent backlash by left-wing vigilantes. But federal agents acting under orders from the White House will have the tactical upper hand in such clashes, which greatly adds to their deterrent capacity.
Finally, an especially strong predictor of election violence is a history of armed political conflict[26]. After the 2016 elections, America experienced massive protests and some rioting[27], but little in the way of deadly political violence.
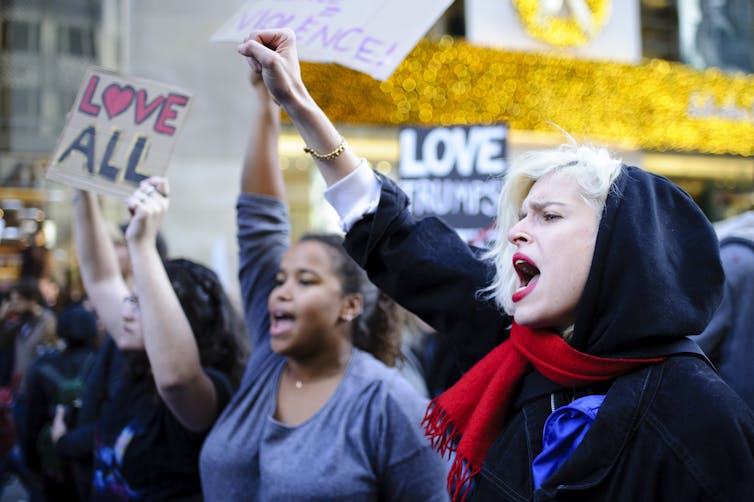 After the 2016 elections, America experienced large protests and some rioting, but little deadly political violence.
David Cliff/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images[28]
After the 2016 elections, America experienced large protests and some rioting, but little deadly political violence.
David Cliff/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images[28]
What the numbers say
Is post-election violence impossible in 2020 America? No.
However, data suggests[29] it is unlikely.
Ninety-five percent of the 12,607 political demonstrations in the U.S. between May 24 and Sept. 19, 2020, were peaceful. There were 351 other kinds of incidents, including imposing curfews and perpetrating physical attacks. In 29 of those, there was violence against civilians, where 12 people were killed, nine of them by the police. And in an additional five drive-by shootings, three police officers were killed by the extremist group the Boogaloo Bois[30].
Considering the number of people involved in the recent Black Lives Matter and COVID-19 protests, and the fact that many were heavily armed[31], these casualty figures are surprisingly low. According to the data[32], the majority of deaths were caused by police, not vigilantes or protesters, and all of the perpetrators (with the exception of two drive-by shooters), police and civilians alike, were taken into custody.
Like the U.S., France experienced protests and riots, in addition to multiple terrorist attacks, prior to Election Day. There was even a government plan[33] to handle the potential violence and instability that might ensue if Le Pen were elected. And yet, as the most polarizing elections in decades concluded, there were few riots and no killing.
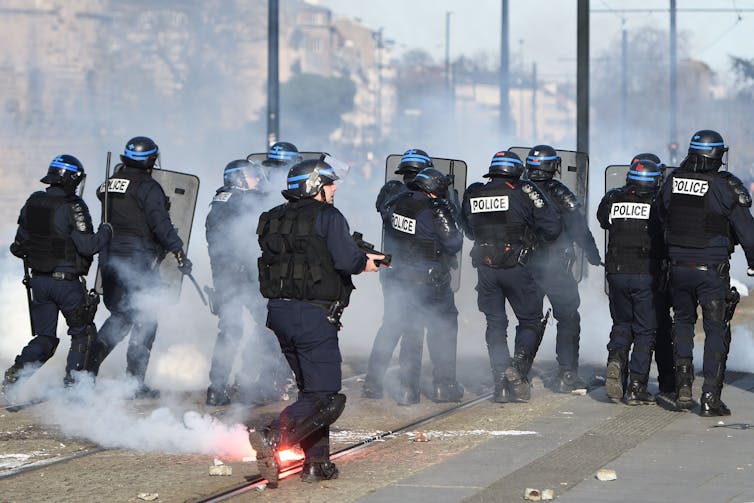 French riot policemen clash with protesters at a demonstration against the presidential candidate for the far-right Front National party, Feb. 25, 2017 in Nantes.
Jean-Sebastien Evrard/AFP via Getty Images[34]
French riot policemen clash with protesters at a demonstration against the presidential candidate for the far-right Front National party, Feb. 25, 2017 in Nantes.
Jean-Sebastien Evrard/AFP via Getty Images[34]
So, what will happen in November?
Researchers cannot perfectly predict political violence. Their analyses rely on the past.
Add to the equation a notoriously unpredictable incumbent[35] against a backdrop of unprecedented social and economic conditions[36], and making accurate predictions about potential post-election bedlam is impossible, as much as scholars and others may try.
[Deep knowledge, daily. Sign up for The Conversation’s newsletter[37].]
While I think some concern is valid, it is important to remember that there is a big difference between using a call to arms to mobilize your voters and instill fear in the other party’s supporters, and staging a post-election insurrection, which could subject its instigators to charges of sedition, if not high treason[38].
Ultimately, the three factors discussed here suggest that fears of widespread violence by vigilantes and activists during and after Election Day should be treated as fears, not as a probable outcome.
References
- ^ protests, riots and ethnic violence (theconversation.com)
- ^ concern that a similar scenario may unfold here (www.vox.com)
- ^ misinformation to mobilize vigilante militias (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ refuse to accept the results and mobilize (time.com)
- ^ as politically polarizing (www.daily-sun.com)
- ^ racist and xenophobic (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ the candidate of savage globalisation (www.bbc.com)
- ^ state of emergency (apnews.com)
- ^ conceded defeat (pittsburgh.cbslocal.com)
- ^ Tony Karumba/AFP/Getty Images (www.gettyimages.com)
- ^ social science researchers like me (polisci.indiana.edu)
- ^ especially effective (onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- ^ President Trump has weakened American political institutions (www.theatlantic.com)
- ^ crises and abuse of presidential power (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ electoral fraud is extremely rare (fivethirtyeight.com)
- ^ the U.S. Supreme Court (theconversation.com)
- ^ House of Representatives (history.house.gov)
- ^ my own (academic.oup.com)
- ^ have no capacity to prevent it (www.jstor.org)
- ^ Mungiki (www.jstor.org)
- ^ well-trained National Guard (theconversation.com)
- ^ violence by vigilantes (theconversation.com)
- ^ federal agencies to seize ballots (www.economist.com)
- ^ formal commitment (www.cnn.com)
- ^ keeping the military nonpoliticized (www.stripes.com)
- ^ history of armed political conflict (academic.oup.com)
- ^ massive protests and some rioting (www.politico.com)
- ^ David Cliff/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images (www.gettyimages.com)
- ^ data suggests (acleddata.com)
- ^ Boogaloo Bois (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ many were heavily armed (theconversation.com)
- ^ the data (acleddata.com)
- ^ There was even a government plan (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ Jean-Sebastien Evrard/AFP via Getty Images (www.gettyimages.com)
- ^ notoriously unpredictable incumbent (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ unprecedented social and economic conditions (time.com)
- ^ Sign up for The Conversation’s newsletter (theconversation.com)
- ^ sedition, if not high treason (www.law.cornell.edu)
Authors: Ore Koren, Assistant Professor, Indiana University Bloomington; International Security Fellow, Indiana University
Read more https://theconversation.com/election-violence-in-november-heres-what-the-research-says-146548

