Postwar forced resettlement of Germans echoes through the decades
- Written by Anil Menon, Ph.D. Candidate in Political Science, University of Michigan
Seventy-five years ago, Allied Forces declared victory in Europe on May 8, 1945. Millions across the continent had been persecuted, displaced and killed because of their national, ethnic or religious backgrounds.
For some, including those Jews and Roma[1] who had survived the Holocaust[2], the war’s end took power away from their persecutors and executioners.
My research traces the history of the roughly 14 million ethnic Germans expelled by national governments across Eastern Europe at the end of World War II, in reaction to the atrocities committed by Nazi Germany. Their suffering would extend into German and European politics all the way to the present.
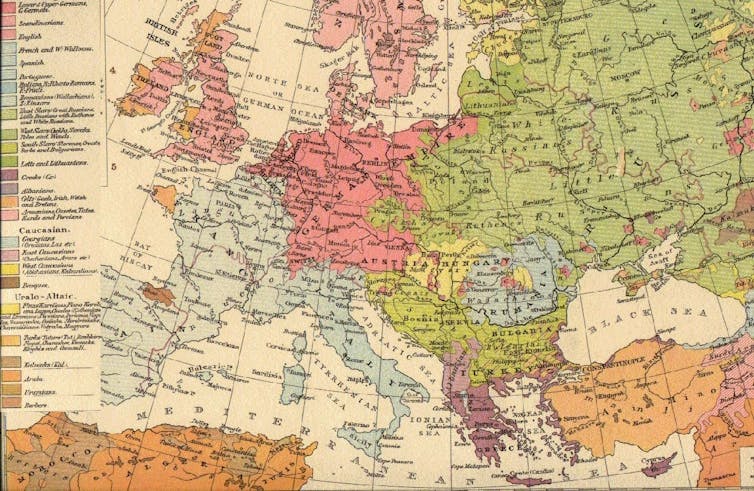 A map from 1896 shows the prevalence of languages spoken across Europe; German (in darker red) is clearly spoken not only in present-day Germany and the surrounding territories, but in enclaves throughout Eastern Europe.
The Times Atlas/Wikimedia Commons[3]
A map from 1896 shows the prevalence of languages spoken across Europe; German (in darker red) is clearly spoken not only in present-day Germany and the surrounding territories, but in enclaves throughout Eastern Europe.
The Times Atlas/Wikimedia Commons[3]
Centuries of history
Going back at least a millennium, people who speak German and follow German cultural traditions had spread across Eastern Europe in waves of conquest and migration. When Europe’s borders were redrawn at the end of World War I, these people became substantial minorities in Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Italy, Poland and Yugoslavia.
Between the two world wars, authorities in Poland and Czechoslovakia confiscated the lands of several thousand ethnic Germans[4], justifying these actions as a response to past injustices[5] the Germans had inflicted on them when ruling those regions.
As he rose to power in Germany, Nazi leader Adolf Hitler championed the notion of a greater German national identity, which appealed to these minority populations living outside Germany’s borders[6]. In the 1930s, the Nazi Party supported like-minded political parties[7] in surrounding countries. The far-right Sudeten German Party, in particular, was able to attract a sizable ethnic German following within Czechoslovakia[8] prior to the onset of war.
During the early days of the war, Polish authorities deported 15,000 ethnic Germans[9] to the east, fearing they would collaborate with Hitler’s forces. War paranoia also resulted in the killing of over 4,000 civilians[10] from this minority population. While many ethnic Germans around Eastern Europe did support the Third Reich, some did take up arms against the Nazi invasion of their countries[11].
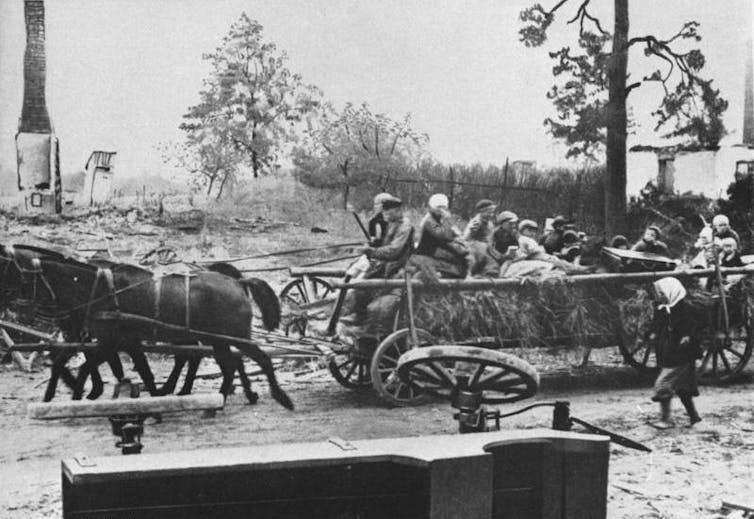 German refugees from East Prussia, 1946.
German Federal Archives/Wikimedia Commons[12]
German refugees from East Prussia, 1946.
German Federal Archives/Wikimedia Commons[12]
A forced relocation
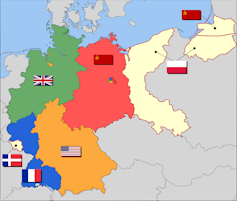 After World War II, the cream-colored areas east of Germany were allocated mostly to Poland, with a little for the Soviet Union.
52 Pickup after IEG-Maps/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA[13][14]
After World War II, the cream-colored areas east of Germany were allocated mostly to Poland, with a little for the Soviet Union.
52 Pickup after IEG-Maps/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA[13][14]
At the Potsdam Conference[15] held in July and August 1945 to plan governance of Europe after the war, the victors – the U.S., the U.K. and the USSR – agreed to shift Germany’s eastern border with Poland westward. As a result, Germany lost about a quarter of the territory it had governed in 1937, before the war began. German citizens in these areas lost their lands, which became part of Poland, with a small portion allocated to the Soviet Union.
At Potsdam, the Allies also agreed to remove ethnic Germans from central and Eastern Europe[16] and consolidate them into the new German state. They hoped this would prevent future conflicts that might arise if sizable German minorities remained within the boundaries of other nations. This forced relocation was to “be effected in an orderly and humane manner[17],” according to the countries’ agreement.
However, violent expulsions had already begun. Europeans who had been conquered, oppressed and persecuted by the Nazis turned their anger toward the ethnic Germans in their own communities, many of whom had lived there for multiple generations.
Across Eastern Europe, ethnic German families were stripped of their land and property, and allowed to take just one suitcase of belongings. Much of their cash and other valuables were confiscated by both government authorities and citizens. In one instance, authorities in the Czech city of Brno forced 20,000 ethnic Germans to walk the roughly 40 miles to the nearest border[18] in May 1945. Some 1,700 of them died on the march.
Between 1944 and 1950, these expulsions resulted in the deaths of over half a million ethnic Germans, with some experts claiming a death toll in excess of two million[19]. Deaths resulted from a variety of causes, including but not limited to malnutrition, disease, physical violence, and time spent in internment camps[20]. By 1950, Eastern Europe contained roughly one-fourth of its prewar ethnic German population[21]. In contrast, the Holocaust killed 6 million Jews, or two-thirds[22] of Europe’s prewar Jewish population, and drove most of the rest of them out of Europe.
 Germans from the Czech region of Sudetenland arrive in Munich on June 15, 1946.
dpa/picture alliance via Getty Images[23]
Germans from the Czech region of Sudetenland arrive in Munich on June 15, 1946.
dpa/picture alliance via Getty Images[23]
Experience in West Germany
Roughly 12 million expelled ethnic Germans made it to postwar Germany. The 4 million who arrived in East Germany did get some social and economic aid from the Soviet authorities, but saw their political activities tightly limited[24].
Meanwhile, in West Germany, the governing Allied military administrations were overwhelmed by these newest European refugees. The devastation of war, including urban bombing and close-quarters fighting, had damaged or destroyed more than 20% of Germany’s prewar houses and apartments[25]. The new arrivals were sent to rural areas, with smaller populations and more housing availability.
Local residents in rural areas had escaped the worst of the war and had a hard time empathizing with the expellees’ suffering. Some of the local residents were forced to house their newly arrived compatriots[26], crowding homes and building tensions between the two groups. Other new arrivals ended up, sometimes for years, in government-run camps described in one report as “absolutely unsuitable for human habitation[27].”
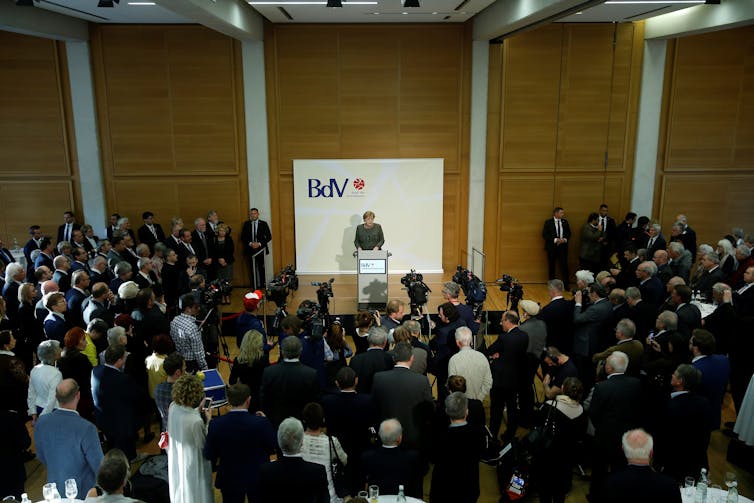 German Chancellor Angela Merkel speaks at the 2019 annual meeting of the Federation of Expellees in Berlin.
Abdulhamid Hosbas/Anadolu Agency/Getty Images[28]
German Chancellor Angela Merkel speaks at the 2019 annual meeting of the Federation of Expellees in Berlin.
Abdulhamid Hosbas/Anadolu Agency/Getty Images[28]
Becoming a political movement
To advocate for their needs, some expellees sought political power, creating a political party called “All-German Bloc/League of Expellees and Deprived of Rights” in 1950[29]. Known by its German acronym, GB/BHE, the party lobbied to improve the economic and social conditions faced by expellees. The GB/BHE won 5.9% of votes in the 1953 federal election[30], making it the fifth-largest party in West Germany.
Its electoral power waned[31] as expellee economic fortunes improved during West Germany’s postwar economic boom[32]. Some leaders from the now defunct GB/BHE helped found[33] the far-right National Democratic Party in 1964. A number of early expellee political leaders also had ties to Nazism, including eight of the 13 founders[34] of the more politically moderate national umbrella group, the Federation of Expellees[35]. Both the Federation and the National Democratic Party are still active today.
The expellees’ cause remained important in German politics. During the 1960s, all the country’s major parties maintained a commitment to reclaiming territories lost under the Potsdam Agreement[36]. However, this demand proved politically unfeasible. The international community held Germany and its people responsible for the Holocaust, and were not interested in fulfilling expellees’ political demands. Mainstream parties gradually abandoned the issue.
 A memorial to the German expellees in Biatorbágy, Hungary.
Globetrotter19/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA[37][38]
A memorial to the German expellees in Biatorbágy, Hungary.
Globetrotter19/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA[37][38]
Expellee concerns have continued to cause tensions between Germany and its Eastern neighbors. In the late 1990s, some expellee groups demanded that Poland and the Czech Republic apologize[39] for their treatment of the expellees before being allowed to join the European Union. In the early 2000s, calls for a museum and archive documenting their fate[40] resulted in tensions with Germany’s eastern neighbors.
In 2019, the right-wing populist party Alternative for Germany created a working group to “preserve the legacy of the German East[41],” keeping the legacy of expulsion active in German politics even to the present day.
[You’re smart and curious about the world. So are The Conversation’s authors and editors. You can get our highlights each weekend[42].]
References
- ^ Roma (www.hmd.org.uk)
- ^ Holocaust (www.britannica.com)
- ^ The Times Atlas/Wikimedia Commons (commons.wikimedia.org)
- ^ confiscated the lands of several thousand ethnic Germans (us.macmillan.com)
- ^ response to past injustices (www.cambridge.org)
- ^ which appealed to these minority populations living outside Germany’s borders (www.jstor.org)
- ^ Nazi Party supported like-minded political parties (www.cambridge.org)
- ^ a sizable ethnic German following within Czechoslovakia (www.cambridge.org)
- ^ deported 15,000 ethnic Germans (us.macmillan.com)
- ^ over 4,000 civilians (yalebooks.yale.edu)
- ^ some did take up arms against the Nazi invasion of their countries (www.jstor.org)
- ^ German Federal Archives/Wikimedia Commons (commons.wikimedia.org)
- ^ 52 Pickup after IEG-Maps/Wikimedia Commons (commons.wikimedia.org)
- ^ CC BY-SA (creativecommons.org)
- ^ Potsdam Conference (www.britannica.com)
- ^ remove ethnic Germans from central and Eastern Europe (www.worldcat.org)
- ^ be effected in an orderly and humane manner (history.state.gov)
- ^ forced 20,000 ethnic Germans to walk the roughly 40 miles to the nearest border (www.dw.com)
- ^ death toll in excess of two million (www.palgrave.com)
- ^ malnutrition, disease, physical violence, and time spent in internment camps (muse.jhu.edu)
- ^ roughly one-fourth of its prewar ethnic German population (www.springer.com)
- ^ 6 million Jews, or two-thirds (encyclopedia.ushmm.org)
- ^ dpa/picture alliance via Getty Images (www.gettyimages.com)
- ^ political activities tightly limited (www.cambridge.org)
- ^ more than 20% of Germany’s prewar houses and apartments (muse.jhu.edu)
- ^ forced to house their newly arrived compatriots (muse.jhu.edu)
- ^ absolutely unsuitable for human habitation (www.google.com)
- ^ Abdulhamid Hosbas/Anadolu Agency/Getty Images (www.gettyimages.com)
- ^ “All-German Bloc/League of Expellees and Deprived of Rights” in 1950 (global.oup.com)
- ^ 1953 federal election (www.bundeswahlleiter.de)
- ^ electoral power waned (www.bundeswahlleiter.de)
- ^ West Germany’s postwar economic boom (muse.jhu.edu)
- ^ helped found (library.fes.de)
- ^ eight of the 13 founders (www.thelocal.de)
- ^ Federation of Expellees (www.bund-der-vertriebenen.de)
- ^ reclaiming territories lost under the Potsdam Agreement (www.jstor.org)
- ^ Globetrotter19/Wikimedia Commons (commons.wikimedia.org)
- ^ CC BY-SA (creativecommons.org)
- ^ demanded that Poland and the Czech Republic apologize (www.csmonitor.com)
- ^ calls for a museum and archive documenting their fate (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ preserve the legacy of the German East (www.afdbundestag.de)
- ^ You can get our highlights each weekend (theconversation.com)
Authors: Anil Menon, Ph.D. Candidate in Political Science, University of Michigan
Read more https://theconversation.com/postwar-forced-resettlement-of-germans-echoes-through-the-decades-137219

