Why the US-Iran conflict isn’t driving oil prices higher – and why it probably should
- Written by Scott L. Montgomery, Lecturer, Jackson School of International Studies, University of Washington
Assassinations, militaries on high alert, geopolitical tensions at the boil. Any one of these in Persian Gulf countries would have roiled oil prices a few years ago. Today, even in combination, they hardly register[1].
Is the oil market now so secure that even the prospect of war between Iran and the U.S. has little effect? More broadly, is this relatively sanguine response[2] warranted at this time?
Reasons oil traders should be nervous
The assassination of Qassem Soleimani, Iran’s top military commander and head of its Revolutionary Guards, happened on Iraqi soil, without Iraqi permission, while Soleimani was reportedly[3] on official business.
This attack by a U.S. drone, which killed up to 10 Iranian and Iraqi personnel, transgressed two nations’ sovereignty. It could be easily defined[4] as an act of war.
Iran did so[5] and responded with a missile barrage[6] at two U.S. bases, apparently causing no casualties. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo, meanwhile, completely rejected[7] Iraq’s demand that American troops leave its soil, only a week after U.S. warplanes carried out lethal attacks[8] on Iran-backed militias in Iraq, also without Iraqi authorization.
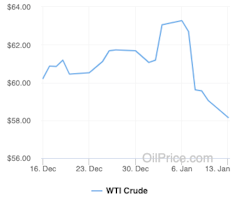 After rising slightly soon after the killing of top Iranian general Quassim Soleimani on Jan. 3, oil prices quickly dropped down.
OilPrice.com, Author provided (No reuse)[9]
After rising slightly soon after the killing of top Iranian general Quassim Soleimani on Jan. 3, oil prices quickly dropped down.
OilPrice.com, Author provided (No reuse)[9]
These are grim new events in a volatile region essential to global oil supply, yet they had no important impact on oil prices. Over a few days, prices went from $US66 per barrel to $69, then down to $65[10]. This isn’t even a hiccup; in a year, it will be invisible on the price curve.
True, President Donald Trump said[11] Iran was “standing down,” and there would be new sanctions, not attacks. Yet this president is notorious for impulsive decisions[12]. Iran, moreover, may take its time in seeking revenge.
And in the midst of military tensions, Iran mistook[13] a commercial airliner for a warplane and shot it down, killing 176. It was a terrible echo of the 1988 downing[14] of an airliner by the U.S. warship Vincennes in another moment of high military anxiety.
Reasons they aren’t
Oil traders therefore have much reason to be nervous. But they aren’t. Why?
A big reason, which I noted in a previous Conversation article[15], is that the global oil market has abundant supply, fed by soaring U.S. production. In under a decade, America has been transformed from a huge importer to a major new exporter. These exports grew[16] from 0.6 million barrels per day in early 2017 to over 4 million by December 2019[17].
For several years, OPEC and Russia have cut their own production[18] to keep prices from falling, due to U.S. supply. Also, oil demand has weakened due to the global economic slowdown[19], caused by the U.S.-China trade war[20], a slumping auto industry[21] and other factors. This has supported a perception that the oil market can absorb almost any shock, even the loss of life in a military exchange.
Experienced observers I know say that a stable oil market is often an oxymoron. A host of churning uncertainties exist just beneath the surface. War in the Gulf, however limited initially, could easily get out of hand – that’s what wars do. No one in the region wants this.
Yet no one is in control of an extremely tense situation that continues to worsen and now involves loss of life. To me, oil prices today do not reflect this reality of risk.
Higher prices would be better for a reason that has nothing to do with geopolitics, too. The world needs less consumption, fewer emissions, and help in its shift to electric transport. Cheap oil will not help.
[ Insight, in your inbox each day. You can get it with The Conversation’s email newsletter[22]. ]
References
- ^ they hardly register (fortune.com)
- ^ sanguine response (markets.businessinsider.com)
- ^ reportedly (www.independent.co.uk)
- ^ easily defined (www.newyorker.com)
- ^ did so (www.aljazeera.com)
- ^ missile barrage (www.businessinsider.com)
- ^ completely rejected (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ lethal attacks (apnews.com)
- ^ OilPrice.com (oilprice.com)
- ^ down to $65 (www.bloomberg.com)
- ^ said (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ impulsive decisions (apnews.com)
- ^ mistook (www.aljazeera.com)
- ^ the 1988 downing (www.stripes.com)
- ^ a previous Conversation article (theconversation.com)
- ^ grew (www.eia.gov)
- ^ over 4 million by December 2019 (www.eia.gov)
- ^ cut their own production (www.reuters.com)
- ^ economic slowdown (blogs.imf.org)
- ^ U.S.-China trade war (theconversation.com)
- ^ auto industry (markets.businessinsider.com)
- ^ You can get it with The Conversation’s email newsletter (theconversation.com)
Authors: Scott L. Montgomery, Lecturer, Jackson School of International Studies, University of Washington

