How your diet contributes to nutrient pollution and dead zones in lakes and bays
- Written by Donald Scavia, Professor Emeritus, School for Environment and Sustainability, University of Michigan
Every year in early summer, scientists at universities, research institutions and federal agencies release forecasts for the formation of “dead zones” and harmful algal blooms in the Gulf of Mexico, the Chesapeake Bay and Lake Erie. This year the outlook is not good[1].
The dead zone that forms annually in the Gulf of Mexico is likely to approach, if not surpass, record size at roughly 7,250 square miles. Another dead zone in the Chesapeake Bay is projected to be within the top 20% recorded over the past 20 years – about 2.1 cubic miles, equivalent to over 3.5 million Olympic-size swimming pools. And Lake Erie is also projected to set records, with almost 50,000 tons of potentially toxic algae.
The key factor driving these forecasts is winter and spring rainfall considerably above normal across the central U.S. The winter of 2018-2019 was the wettest on record[2] across the nation, and May was the second-wettest month on record[3].
Predicting the results isn’t rocket science. More rain means more flooding and more runoff from farmlands. These waters carry heavy loads of nutrients, mainly from fertilizer, that fuel algal blooms. The end results include fish kills, closed beaches, possible drinking water alerts and loss of coastal property value[4].
Water in the Gulf of Mexico dead zone can contain less than half of the oxygen levels needed to support fish.Treading water
Algal blooms occur when water bodies become overloaded with nitrogen and phosphorus from farms, water treatment plants and other sources. Warm water and nutrients promote rapid growth of algae. Some strains can be toxic or even fatal to aquatic life and humans.
Eventually algae settle to the bottom and decay. This process depletes dissolved oxygen in the water, creating “dead zones” where oxygen levels are low enough to kill fish.
Scientists and public officials have understood this problem for decades, but progress toward addressing it has been painfully slow. Nutrient loads, dead zones and harmful algal blooms in these systems dominated by agriculture have increased or held grudgingly steady for decades[5].
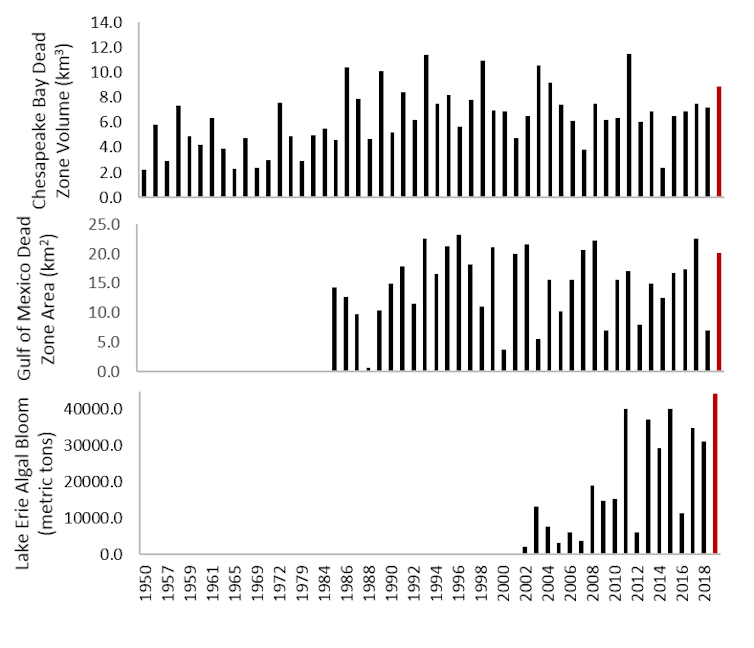 Dead zone and harmful algal bloom trends with 2019 forecasts in red.
from http://scavia.seas.umich.edu/hypoxia-forecasts/
Dead zone and harmful algal bloom trends with 2019 forecasts in red.
from http://scavia.seas.umich.edu/hypoxia-forecasts/
The main policy tool available now to combat nutrient losses from agricultural lands is the Farm Bill[6], enacted about every five years, which provides funds for voluntary conservation efforts[7]. Between 1995 and 2015, the U.S. Department of Agriculture provided almost US$32 billion[8] in conservation incentive payments. U.S. water quality would be much worse without these programs, but they simply have not been sufficient to reduce nutrient loads over time.
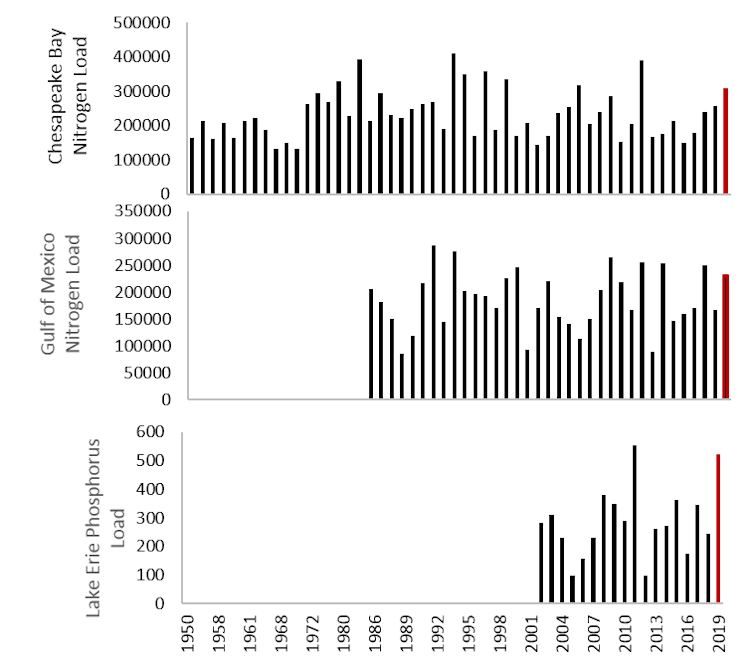 Nutrient load trends; 2019 loads in red.
From: http://scavia.seas.umich.edu/hypoxia-forecasts/
Nutrient load trends; 2019 loads in red.
From: http://scavia.seas.umich.edu/hypoxia-forecasts/
Warmer and wetter
Scientists predict that as the climate warms, this problem is likely to get worse[9].
Most climate models forecast increased precipitation[10], especially intense spring rains, for most of the Midwest, the Great Lakes basin and the mid-Atlantic. As air warms, it can hold increasing amounts of water vapor, which contributes to more precipitation[11] during extreme weather events. In turn, heavier rainfall will impact nutrient runoff and dead zone formation.
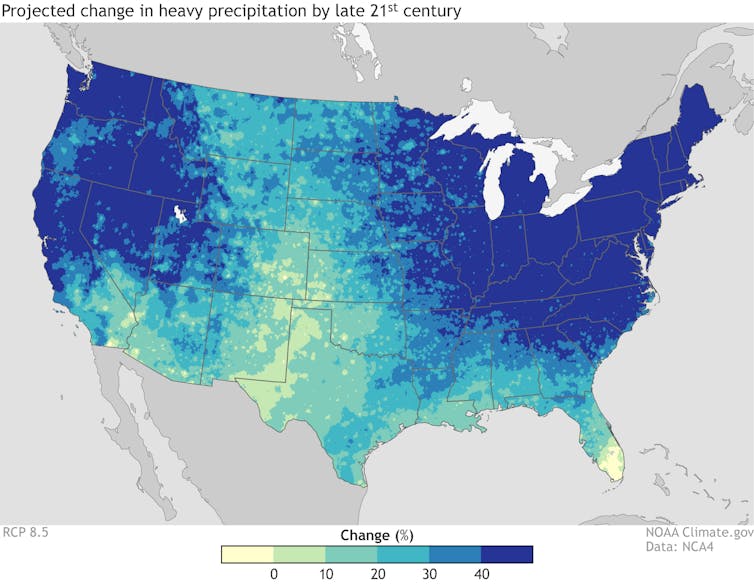 Under a worst-case climate change scenario, in which global temperatures rise nearly 5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels by 2100, very heavy precipitation events in the Midwest, Great Plains and Southeast regions would increase sharply.
NOAA[12]
Under a worst-case climate change scenario, in which global temperatures rise nearly 5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels by 2100, very heavy precipitation events in the Midwest, Great Plains and Southeast regions would increase sharply.
NOAA[12]
A dietary strategy
Farm-based conservation programs are important, and some new practices could improve nutrient management[13]. For example, farmers can widen drainage ditches to create two-stage ditches, which allow water to flow onto vegetated side “benches” that capture nutrients during periods of heavy rainfall.
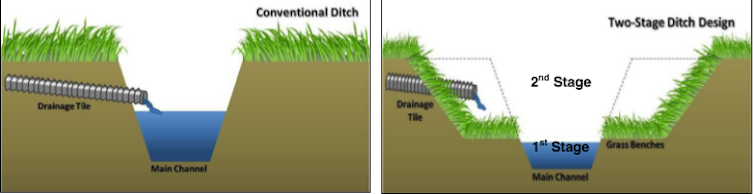 A two-stage ditch has a low-flow channel and a vegetated side ‘benches’ that are flooded during higher flows. The grass slows water flow and allows nutrients to settle out.
Ohio State University Extension, CC BY[14][15]
A two-stage ditch has a low-flow channel and a vegetated side ‘benches’ that are flooded during higher flows. The grass slows water flow and allows nutrients to settle out.
Ohio State University Extension, CC BY[14][15]
But even these measures would have to be implemented at unprecedented scales[16] to be effective. The challenge is even more daunting when recognizing that, for example, while the annual total phosphorus load to Lake Erie is large, it is only 10% of the amount applied in fertilizer each year. In addition, as with the Chesapeake and Mississippi watersheds, soils around Lake Erie are already laden with nitrogen and phosphorus.
In my view, part of the solution could be using markets to drive a shift away from industrial-scale corn production[17], which is a major source of nutrient pollution. One major step would be eliminating the federal mandate requiring oil companies to blend corn-based ethanol into gasoline[18], which consumes 40% of U.S. corn production[19].
This will be politically difficult as long as presidential primaries start in Iowa[20]. But other strategies may be more feasible, such as encouraging private-sector companies to demand corn raised through more sustainable practices[21].
Reducing meat consumption[22], which consumes another 36% of U.S. corn production[23] for animal feed, could also have a significant impact. Studies have shown that reducing this demand for row crops reduces nutrient pollution[24].
This idea has gained momentum with the growth of the alternative meat industry. The success of startups like Beyond Meat[25] and Impossible Foods[26] is luring giants like Tyson[27] and Perdue[28] into the game. Some are even struggling to keep up with demand for plant-based meat alternatives, particularly in China[29]. One recent market analysis suggests that plant-based “meat” will surpass animal sources globally by 2040[30].
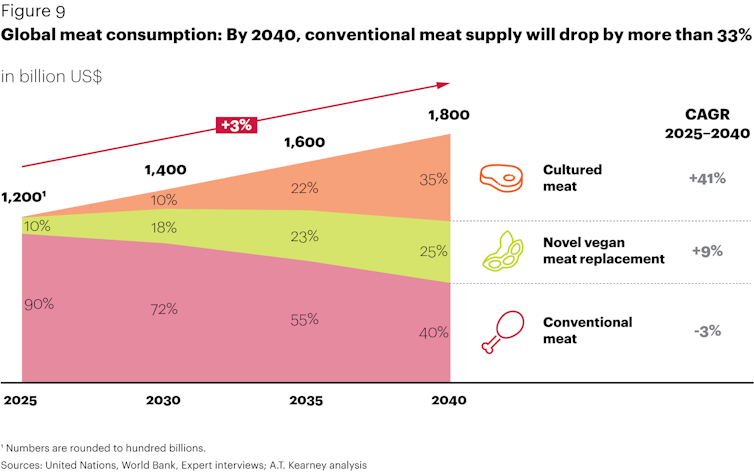 AT Kearney, CC BY-ND[31][32]
Shrinking agriculture’s footprint
Scientists have understood for decades that excess nitrogen and phosphorus degrade Lake Erie, the Chesapeake Bay and the Gulf of Mexico. Nutrient inputs from sewage treatment plants and other discreet, easily identifiable sources have declined because they are regulated under the Clean Water Act.
But the nutrients fouling these water bodies now come mostly from diffuse sources, particularly industrial-scale row crop agriculture. Those operations are not subject to the Clean Water Act, and voluntary conservation programs seem to have at best kept pace with the expansion of large-scale farming.
After analyzing these issues and providing policy advice on them for much of my 45-year career, it’s frustrating to see so little change. But I am hopeful that current work that addresses agricultural pollution in broader contexts may have an impact.
For example, recent reports connecting reduced meat consumption[33] to both positive environmental effects and improved health should provide additional incentives for change. Research institutes[34] and scholars[35] are laying out comprehensive global pathways to more sustainable agriculture that are designed to feed the world and protect and restore natural ecosystems.
My hope lies in the combination of health- and market-driven movement toward plant-based meat substitutes and enlightened policies that support more sustainable practices in agriculture’s critical role of providing food and fiber to the world.
AT Kearney, CC BY-ND[31][32]
Shrinking agriculture’s footprint
Scientists have understood for decades that excess nitrogen and phosphorus degrade Lake Erie, the Chesapeake Bay and the Gulf of Mexico. Nutrient inputs from sewage treatment plants and other discreet, easily identifiable sources have declined because they are regulated under the Clean Water Act.
But the nutrients fouling these water bodies now come mostly from diffuse sources, particularly industrial-scale row crop agriculture. Those operations are not subject to the Clean Water Act, and voluntary conservation programs seem to have at best kept pace with the expansion of large-scale farming.
After analyzing these issues and providing policy advice on them for much of my 45-year career, it’s frustrating to see so little change. But I am hopeful that current work that addresses agricultural pollution in broader contexts may have an impact.
For example, recent reports connecting reduced meat consumption[33] to both positive environmental effects and improved health should provide additional incentives for change. Research institutes[34] and scholars[35] are laying out comprehensive global pathways to more sustainable agriculture that are designed to feed the world and protect and restore natural ecosystems.
My hope lies in the combination of health- and market-driven movement toward plant-based meat substitutes and enlightened policies that support more sustainable practices in agriculture’s critical role of providing food and fiber to the world.
References
- ^ the outlook is not good (scavia.seas.umich.edu)
- ^ wettest on record (www.noaa.gov)
- ^ second-wettest month on record (www.ncei.noaa.gov)
- ^ fish kills, closed beaches, possible drinking water alerts and loss of coastal property value (www.thegazette.com)
- ^ increased or held grudgingly steady for decades (theconversation.com)
- ^ Farm Bill (www.farmers.gov)
- ^ funds for voluntary conservation efforts (theconversation.com)
- ^ US$32 billion (conservation.ewg.org)
- ^ likely to get worse (dx.doi.org)
- ^ increased precipitation (nca2018.globalchange.gov)
- ^ contributes to more precipitation (theconversation.com)
- ^ NOAA (www.climate.gov)
- ^ improve nutrient management (doi.org)
- ^ Ohio State University Extension (agbmps.osu.edu)
- ^ CC BY (creativecommons.org)
- ^ unprecedented scales (dx.doi.org)
- ^ drive a shift away from industrial-scale corn production (theconversation.com)
- ^ blend corn-based ethanol into gasoline (www.epa.gov)
- ^ 40% of U.S. corn production (www.scientificamerican.com)
- ^ start in Iowa (www.politico.com)
- ^ corn raised through more sustainable practices (fieldtomarket.org)
- ^ Reducing meat consumption (www.wri.org)
- ^ 36% of U.S. corn production (www.scientificamerican.com)
- ^ reduces nutrient pollution (doi.org)
- ^ Beyond Meat (www.beyondmeat.com)
- ^ Impossible Foods (impossiblefoods.com)
- ^ Tyson (fortune.com)
- ^ Perdue (www.channelnewsasia.com)
- ^ particularly in China (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ surpass animal sources globally by 2040 (www.atkearney.com)
- ^ AT Kearney (www.atkearney.com)
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ reduced meat consumption (doi.org)
- ^ Research institutes (www.wri.org)
- ^ scholars (doi.org)
Authors: Donald Scavia, Professor Emeritus, School for Environment and Sustainability, University of Michigan

