Atlantic hurricane season starts June 1 – here's what forecasters are watching right now
- Written by Kristopher Karnauskas, Associate Professor of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences and Fellow of the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences, University of Colorado Boulder
As summer in the Northern Hemisphere approaches, forecasters begin watching every bout of rainy weather between the Gulf of Mexico and Africa. Each counterclockwise swirl of wind or burst of puffy clouds there has the potential to organize into a life-threatening tropical storm.
About half of the tropical storms[1] that formed over the past two decades grew into hurricanes, and about half of those became the monsters of coastal destruction we call major hurricanes. We’re now accustomed to seeing about 16 tropical storms per year, though that number can vary quite a bit year to year.
What are the warning signs that we might be in for another record hurricane season like 2020, when 30 tropical storms formed, or a quieter one like 2014, with just eight?
The National Hurricane Center will be issuing its first seasonal forecast of 2021 this week. Here are some of the ingredients forecasters and scientists like myself[2] look for.
Where tropical storms begin
Hurricanes live in the atmosphere, but they are fed by the ocean. First, let’s look even farther upstream and find out where they come from.
Like growing crops, hurricanes will be plentiful and robust with a large number of seeds and favorable environmental conditions.
The seeds of tropical storms are small and hardly menacing weather disturbances. You’ll find them scattered throughout the tropics on any given day. In the Atlantic, some start as clusters of thunderstorms over Africa, or as clouds near the Cape Verde Islands off Africa’s west coast.
The vast majority of these seeds do not survive beyond a few days, but some are swept up by the easterly airflow to be planted over the tropical Atlantic Ocean between about 10 to 20 degrees north latitude. This is the field where growth is really fueled by the ocean. From there, developing tropical storms are carried westward and northward by the “steering currents” of the atmosphere – avoiding the equator where the crucial effect of Earth’s rotation[3] is too small for them to develop further.
The more seeds, the better chance of an active hurricane season.
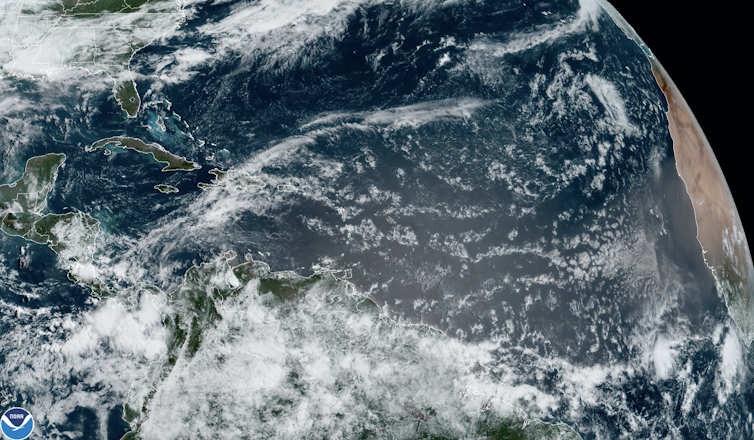 Puffs of clouds off Africa have the potential to become tropical storms.
NOAA[4]
Puffs of clouds off Africa have the potential to become tropical storms.
NOAA[4]
Several factors influence the level of tropical storm seeding in a given year, but forecasters’ eyes are usually trained on the African monsoon[5] in the spring.
Once those seeds emerge from the African coastline or from pockets of warm, rising air popping up elsewhere over the ocean, attention shifts to the environmental conditions that can fuel or limit their growth into tropical storms and hurricanes.
Warm water fuels hurricanes
In general, tropical storms thrive where the surface ocean is a balmy 80 F (26.7 C) or warmer[6]. That’s why hurricanes are rare before June 1 and are most likely to occur August through October, when the ocean is at its warmest.
The main fuel supply for tropical storms is the heat energy[7] in the upper ocean, the top 100 feet (30 meters) or so.
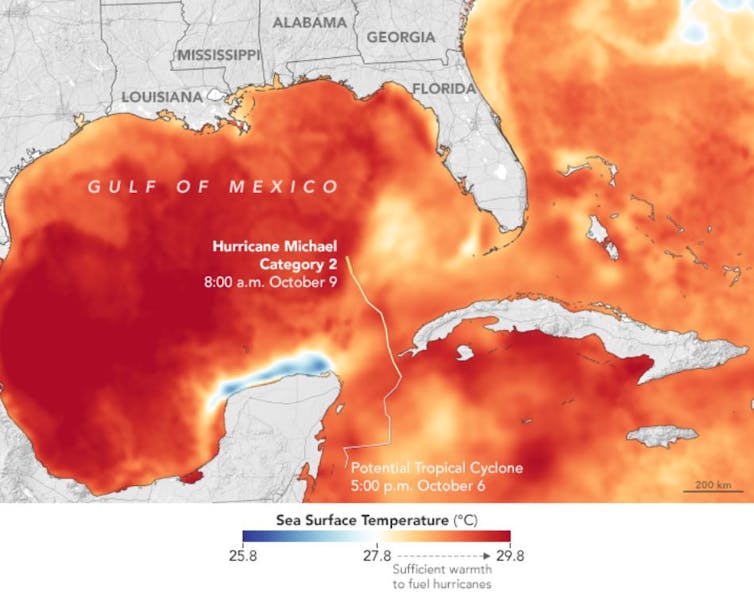 Warm water helped Hurricane Michael grow into a huge, destructive storm in 2018.
NASA Earth Observatory[8]
Warm water helped Hurricane Michael grow into a huge, destructive storm in 2018.
NASA Earth Observatory[8]
It’s more than just the temperature of the surface, though. A major factor in the development of very strong hurricanes is how deep the warm waters extend, and how sharply separated the warm layer is from the cold waters below. This is because hurricanes churn up the ocean as they move along.
If the layer of warm water is shallow and easily mixed, it doesn’t take much churning to dilute the heat energy at the surface with cold water from below, leaving less energy for the hurricane. But if the warm water goes deeper, the storms have more fuel to draw from.
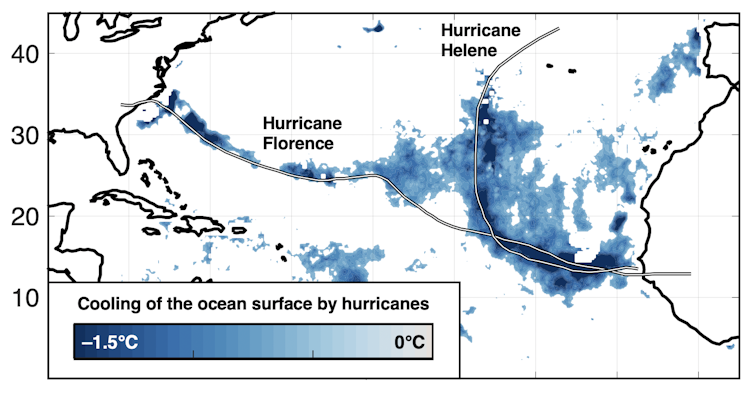 Hurricanes mix the ocean water as they move, leaving a cooler wake in the warm surface water.
Karnauskas, Zhang, and Emanuel 2021, CC BY-ND[9][10]
Hurricanes mix the ocean water as they move, leaving a cooler wake in the warm surface water.
Karnauskas, Zhang, and Emanuel 2021, CC BY-ND[9][10]
The effect of upper-level winds
The prevailing winds already blowing in a region can also make or break a storm.
Winds blow at different speeds at different heights. It’s one of the reasons airplanes experience turbulence. How much faster the prevailing winds are near the top of the storm than at the bottom is called wind shear[11]. With too much wind shear, the storm has difficulty maintaining those towering plumes of rising hot air.
Similarly, if the rising air can’t escape and flow outward quickly enough[12], the energy consumed by the storm can’t be ventilated and the engine chokes. Both can prevent the storm from becoming organized and either cap its growth or cause it to dissipate.
 How El Niño and its opposite, La Niña, affect hurricanes.
NOAA Climate.gov[13]
How El Niño and its opposite, La Niña, affect hurricanes.
NOAA Climate.gov[13]
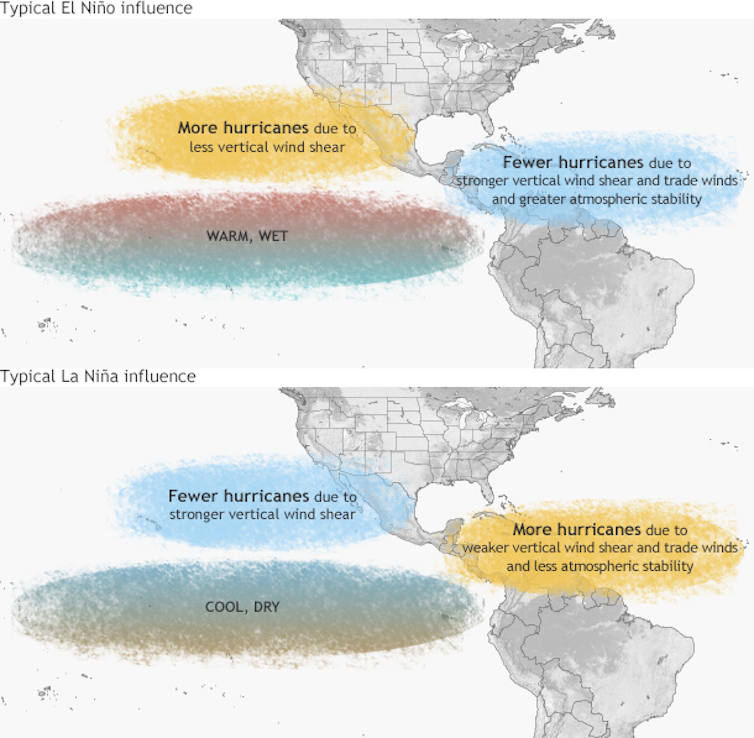
An important clue about future wind shear[14] in the Atlantic region comes from events thousands of miles away in the equatorial Pacific Ocean[15].
When the eastern Pacific Ocean is abnormally warm – known as El Niño[16] – the global atmosphere gets rearranged[17] in a way that increases wind shear over the Atlantic. That tends to suppress tropical storms there – but don’t bet the farm on it. Other slow variations in the climate system also influence environmental conditions, including multi-year periods of warmer or cooler than normal[18] surface temperatures in the North Atlantic.
El Niño’s opposite, La Niña, tends to bring low wind shear, favoring more tropical storms. These conditions are near neutral right now, and forecasters are watching to see what develops.
Where to watch
So if you’re watching for early signs of Atlantic hurricanes in 2021, keep an eye on the African monsoon[19] for storm seeding, temperatures in the tropical Atlantic Ocean[20] to provide the fuel and a possible late-blooming La Niña[21], meaning less wind shear to tear storms apart. The National Hurricane Center[22] – and many other forecasting groups[23] in government, academia and industry – analyze these and other factors in their season projections.
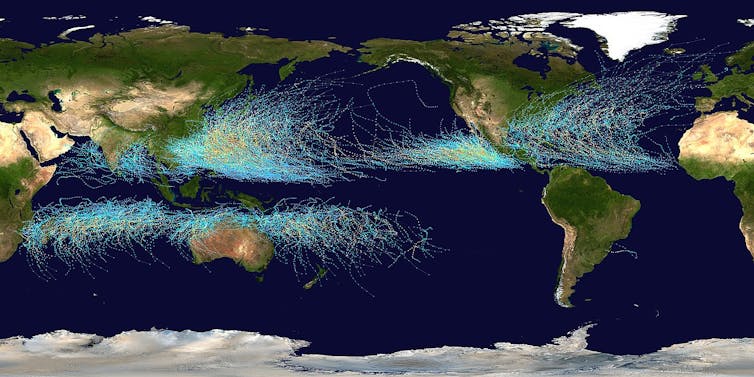 Twenty years of National Hurricane Center storm track data show patterns.
Nilfanion[24]
Twenty years of National Hurricane Center storm track data show patterns.
Nilfanion[24]
The bigger picture
The total number of tropical storms tells only part of the story. There are other important aspects to keep an eye on over time, like how intense storms become[25], how long they last, how fast they travel[26] and how long they take to dissipate after making landfall[27]. Recent studies have indicated that hurricane-fueling ocean temperatures have been trending warmer since the Industrial Revolution, especially along the U.S. East Coast[28].
Coastal communities are already on the front lines of climate change[29] with sea level rise. The potential for changes in extreme events like tropical storms, with their complex interactions with the atmosphere and ocean, are why hurricanes have steadily risen to be a top research priority[30].
[Like what you’ve read? Want more? Sign up for The Conversation’s daily newsletter[31].]
References
- ^ tropical storms (www.nhc.noaa.gov)
- ^ like myself (www.colorado.edu)
- ^ effect of Earth’s rotation (scijinks.gov)
- ^ NOAA (www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov)
- ^ African monsoon (svs.gsfc.nasa.gov)
- ^ balmy 80 F (26.7 C) or warmer (oceanexplorer.noaa.gov)
- ^ fuel supply for tropical storms is the heat energy (ocean.si.edu)
- ^ NASA Earth Observatory (earthobservatory.nasa.gov)
- ^ Karnauskas, Zhang, and Emanuel 2021 (doi.org)
- ^ CC BY-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ wind shear (www.aoml.noaa.gov)
- ^ escape and flow outward quickly enough (blog.weatherflow.com)
- ^ NOAA Climate.gov (www.climate.gov)
- ^ clue about future wind shear (www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov)
- ^ equatorial Pacific Ocean (www.climate.gov)
- ^ El Niño (www.climate.gov)
- ^ gets rearranged (www.climate.gov)
- ^ warmer or cooler than normal (www.noaa.gov)
- ^ African monsoon (svs.gsfc.nasa.gov)
- ^ temperatures in the tropical Atlantic Ocean (psl.noaa.gov)
- ^ a possible late-blooming La Niña (iri.columbia.edu)
- ^ National Hurricane Center (www.nhc.noaa.gov)
- ^ many other forecasting groups (seasonalhurricanepredictions.bsc.es)
- ^ Nilfanion (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ how intense storms become (www.gfdl.noaa.gov)
- ^ how fast they travel (doi.org)
- ^ how long they take to dissipate after making landfall (doi.org)
- ^ especially along the U.S. East Coast (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ front lines of climate change (nca2018.globalchange.gov)
- ^ top research priority (www.wcrp-climate.org)
- ^ Sign up for The Conversation’s daily newsletter (theconversation.com)
Authors: Kristopher Karnauskas, Associate Professor of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences and Fellow of the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences, University of Colorado Boulder

