Post-election grief is real, and here are 5 coping strategies – including getting back into politics
- Written by Christopher Ojeda, Assistant Professor of Political Science, University of Tennessee
Shortly after Abraham Lincoln was elected on Nov. 6, 1860, a woman from Alabama, Sarah Espy, documented her concerns in her diary. She wrote[1] that she felt “grieved,” and explained why. “For it is thought now to be certainty that Lincoln…and that the Southern States are going to withdraw from the Union. If so, it is the beginning of woe.”
While the particular concerns change, every election triggers distress for some people. That certainly held true for the previous two presidential elections: Many Americans were deeply upset following the victories of Barack Obama[2] in 2008 and of Donald Trump[3] in 2016.
Symptoms of depression – sadness, loneliness and fatigue – seem to be common responses to electoral loss.[4] This may prove to be a particularly widespread phenomenon in the aftermath of the 2020 election, given the nation’s contentious political divide[5].
People don’t typically talk about politics in the same sentence as grief and woe, but the two are more closely connected than we might realize. I am a political scientist[6] who studies how mental health shape the way citizens think and engage with politics. In my work[7] as a political scientist, I’ve found that citizens who suffer from depression are less politically engaged. I’m currently exploring how politics impact citizens’ mental health, especially in the wake of an election.
The politics of depression
Psychologists have long recognized depression as a frequent response to loss. Elisabeth Kübler-Ross[8] famously named it as one of the five stages of grief, along with denial, anger, bargaining and ultimately, acceptance. Other research has since questioned this concept of stages[9], finding instead that some people experience just one or two of these emotions[10].
While scholars have written about anger[11] and denial[12] in relation to politics, we know far less about depression. Evidence I’ve compiled suggests it’s relatively common.
For example, a 2004 Pew Research Center survey[13] found that 29% of Kerry supporters felt depressed in the wake of George Bush’s reelection and a 2008 Associated Press poll[14] found 25% of Republicans were upset following the election of Barack Obama. Polling data from 2010, 2012 and 2016 reveal similar results.
This data captures the intensity of emotions we feel from electoral loss. The website PsychCentral[15] noted that traffic to their “5 Stages of Grief & Loss” page was up by 210% the day after Hillary Clinton lost the election in 2016 – and their most popular article was “Healing after the Election[16].” Similarly, Google Trends[17] data on grief-related searches spiked following the 2008 and 2016 elections.
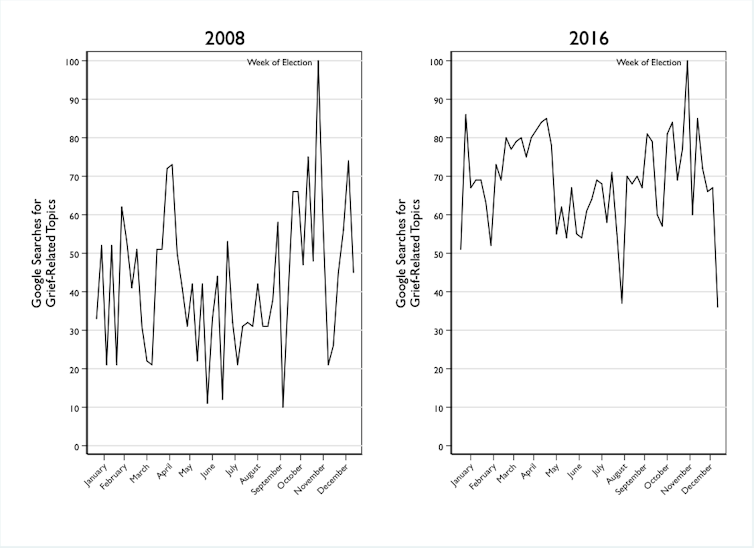 Grief-related searches on Google spiked after the 2008 and 2016 U.S. presidential elections.
Google Trends, Author provided
Grief-related searches on Google spiked after the 2008 and 2016 U.S. presidential elections.
Google Trends, Author provided
The evidence is clear: Many Americans feel depressed after elections.
Coping with post-election blues
There is no easy way to make depression disappear, but there are actions we can take to cope.
Focusing on healthy living will help restore your energy. Give yourself breaks from the news – and politics. Get enough sleep, eat well and get some exercise.
Limit time on social media[18], or better yet, log off altogether for a few days. While it’s a way to connect with other people and share information, it’s also a key source of political misinformation, echo chamber conversations and polarized thinking. Overall, too much time on Facebook or Twitter can intensify anxiety and depression[19].
Seek out social support. Talk to a trusted family member, friend, community leader – or find a social support group in your area. While that may be a bit more challenging in a pandemic, with the need for social distancing, it’s still possible to pick up the phone, get on a FaceTime call or set up a virtual appointment with a mental health professional. But also remember Goldilocks’ rule[20]: Social isolation intensifies negative feelings, but so does spending too much time talking about problems.
Affirm the value of democracy. Electoral loss is scary because it means having to contend with unwanted or disliked policies – and can create extreme polarization. But accepting loss is part and parcel of democracy[21]. One way to bridge political differences[22] is to join a group, such as Building Bridgers[23], which brings together citizens with diverse political views to engage in structured conversations.
Once you’ve accepted the outcome, get involved with politics. Elections are just the start of what is a complex policymaking process. Participating is empowering and can help alleviate psychological distress[24]. There are many ways to contribute, from contacting elected officials, protesting, running for local office or donating money to joining advocacy organizations or starting a political discussion group.
Ultimately, democratic societies select leaders through voting, but one unsavory part of the process is that many citizens don’t get their preferred choice.
Being on the losing side of an election may create distrust in the system and dissatisfaction with democracy. My research shows that it hits us emotionally, too. But instead of letting hurt sideline you from politics, use it to fuel the passion you felt before the election.
[Understand new developments in science, health and technology, each week. Subscribe to The Conversation’s science newsletter[25].]
References
- ^ wrote (www.cambridge.org)
- ^ Barack Obama (www.cnn.com)
- ^ Donald Trump (www.businessinsider.com)
- ^ to be common responses to electoral loss. (psychcentral.com)
- ^ contentious political divide (www.pewresearch.org)
- ^ political scientist (polisci.utk.edu)
- ^ In my work (www.cambridge.org)
- ^ Elisabeth Kübler-Ross (www.simonandschuster.com)
- ^ questioned this concept of stages (journals.sagepub.com)
- ^ experience just one or two of these emotions (jamanetwork.com)
- ^ anger (www.cambridge.org)
- ^ denial (www.journals.uchicago.edu)
- ^ survey (www.pewresearch.org)
- ^ poll (www.denverpost.com)
- ^ PsychCentral (psychcentral.com)
- ^ Healing after the Election (psychcentral.com)
- ^ Google Trends (trends.google.com)
- ^ social media (papers.ssrn.com)
- ^ can intensify anxiety and depression (guilfordjournals.com)
- ^ Goldilocks’ rule (www.apa.org)
- ^ part and parcel of democracy (oxford.universitypressscholarship.com)
- ^ bridge political differences (theconversation.com)
- ^ Building Bridgers (www.buildingbridgers.com)
- ^ is empowering and can help alleviate psychological distress (staging.nonprofitvote.org)
- ^ Subscribe to The Conversation’s science newsletter (theconversation.com)
Authors: Christopher Ojeda, Assistant Professor of Political Science, University of Tennessee

