How being 'tough on crime' became a political liability
- Written by Jody D. Armour, Roy P. Crocker Professor of Law, University of Southern California
Kamala Harris recently dropped out of the presidential race after months of attacks from the left[1] for her “tough-on-crime” record as San Francisco’s district attorney and as California’s attorney general.
A few years ago, the idea that being tough on crime would be a liability – not an asset – was unthinkable for both Democrats and Republicans.
Bill Clinton, during the 1992 presidential race, interrupted his campaign so he could return to Arkansas to witness the execution of a mentally disabled man[2]. During Harris’ 2014 reelection campaign for attorney general, she actively sought – and won – the endorsements of more than 50 law enforcement groups[3] en route to a landslide victory[4].
But something has changed in recent years. Harris’ failure to gain traction as a presidential candidate has coincided with a growing number of “progressive prosecutors.”
In the past, I would have scoffed at the notion of a progressive prosecutor. It would have seemed like a ridiculous oxymoron.
But in one of the most stunning shifts in American politics in recent memory, a wave of elected prosecutors have bucked a decadeslong tough-on-crime approach adopted by both major parties. These prosecutors are refusing to send low-level, non-violent offenders to prison, diverting defendants into treatment programs, working to eradicate the death penalty and reversing wrongful convictions.
The unchecked power of prosecutors
In 1968, when I was 8 years old, my father was sentenced to 22 to 55 years in the Ohio State Penitentiary for the possession and sale of marijuana. During the trial, the district attorney had repeatedly assured the jurors that he hadn’t promised the state’s principal witness – then serving a long sentence – leniency in return for testifying against my father.
In truth, they had struck that very bargain. After studying the warden’s own law books, my father appealed the conviction, representing himself. He was ultimately vindicated by the 6th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals[5] after proving that the district attorney had deliberately lied to the jury.
That was in 1974. I went on to become a lawyer and law professor[6]. During the years I spent teaching and studying the relationship between race and the law, the prison population exploded[7], and my distrust toward government prosecutors only deepened. Too often, it seemed like they were bringing excessively punitive charges in order to force defendants into plea deals[8]. Too often, their approach seemed to reflect a longing for retribution and revenge rather than rehabilitation.
In 2017, law professor John Pfaff was able to show[9] that mass incarceration was due, first and foremost, to the nearly unchecked power of district attorneys.
With reported crimes and arrests steadily declining in the 1990s and 2000s[10], you might have expected incarceration rates to also fall. Instead, they soared. Pfaff traces this perplexing trend to one key statistic[11]: Between 1994 and 2008, the probability that a district attorney would file a felony charge against someone who’s been arrested roughly doubled[12], from about 1 in 3 to nearly 2 in 3.
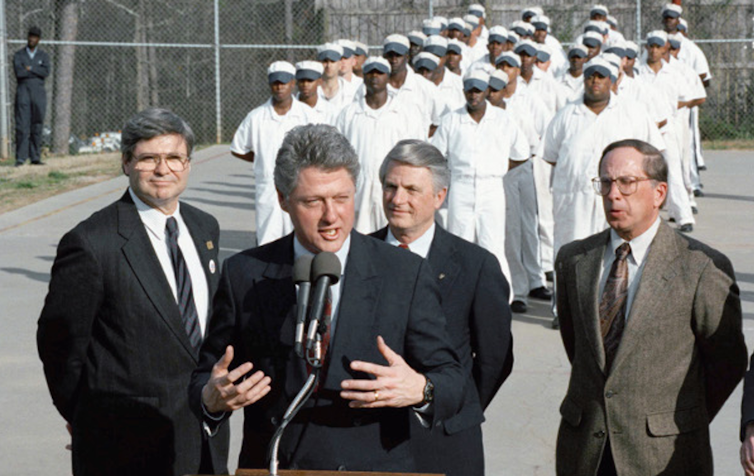 To some voters, the Democratic Party’s approach to criminal justice under Bill Clinton hasn’t aged well.
Current Affairs[13]
To some voters, the Democratic Party’s approach to criminal justice under Bill Clinton hasn’t aged well.
Current Affairs[13]
More than stiff drug laws, punitive judges, overzealous cops or private prisons, prosecutors had been the main drivers[14] of a prison population[15] that had quadrupled since the mid-1980s.
Meanwhile, black Americans continued to be disproportionately incarcerated. In 2017, there were 1,549 black prisoners for every 100,000 black adults – nearly six times[16] the incarceration rate for whites and nearly double the rate for Hispanics.
This prosecutorial approach wasn’t punished at the ballot box; instead, racking up convictions and plea deals seemed to bolster the political careers of district attorneys[17].
The new sheriffs in town
No longer.
Since 2013, roughly 30 reform-minded prosecutors have been elected. A few now preside over prosecutorial staffs in some of the nation’s biggest cities, like Philadelphia’s Larry Krasner[18] and Boston’s Rachael Rollins[19]. But they also include chief prosecutors of smaller municipalities, like Satana Deberry[20], who was elected district attorney of Durham County, North Carolina, in 2018, and Parisa Dehghani-Tafti[21], the commonwealth’s attorney of Arlington County, Virginia, who won on a platform of ending mass incarceration in 2019.
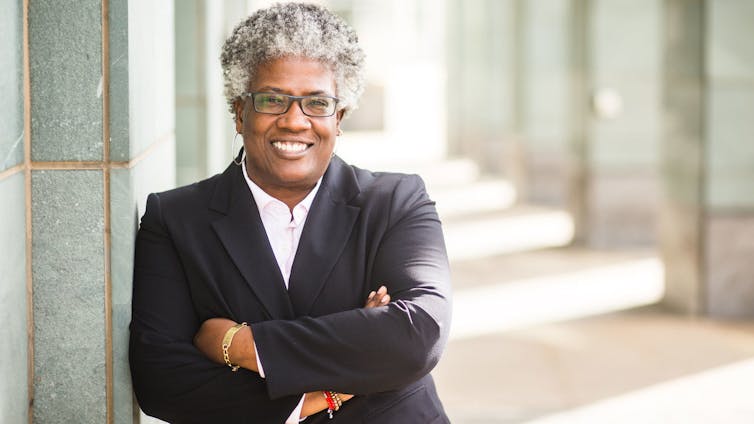 Satana Deberry won her district attorney race in 2018 by campaigning on ending cash bail.
Satana Deberry[22]
Satana Deberry won her district attorney race in 2018 by campaigning on ending cash bail.
Satana Deberry[22]
These prosecutors are reinventing the role of the modern district attorney. Krasner, for example, campaigned on[23] eliminating cash bail, reining in police misconduct and upending a system of mass incarceration that disproportionately imprisons people of color. He won with nearly 75% of the vote[24] in the general election.
In 2018, before a packed lecture hall, Krasner told my law students[25] that ending racialized mass incarceration is “the most important civil rights issue of our time.” He pointed out that the key difference between a traditional prosecutor and progressive one is that the latter is a “prosecutor with compassion” and “a public defender with power.”
This growing crop of “prosecutors with compassion” and “public defenders with power” has upended my own binary way of thinking about the role of the district attorney.
I’ve realized that a district attorney can adopt a fundamentally different moral compass and conception of justice. While traditional “law and order” prosecutors possess a moral, legal and political compass that sharply distinguishes between victims and perpetrators, I’d argue that truly progressive prosecutors recognize that “hurt people hurt people[26]” and refuse to subordinate the values of restoration, rehabilitation and redemption to those of retribution, retaliation and revenge.
These two sets of values can collide. Many entrenched judges, prosecutors, police chiefs, police unions and legislators have loudly opposed – or have actively resisted – this shift to restoration and redemption.
Progressive prosecutors, according to U.S. Attorney General William Barr[27], are “undercutting the police, letting criminals off the hook, and refusing to enforce the law.” In a December rally, President Trump singled out Krasner[28], calling him “the worst district attorney,” one who “lets killers out almost immediately.”
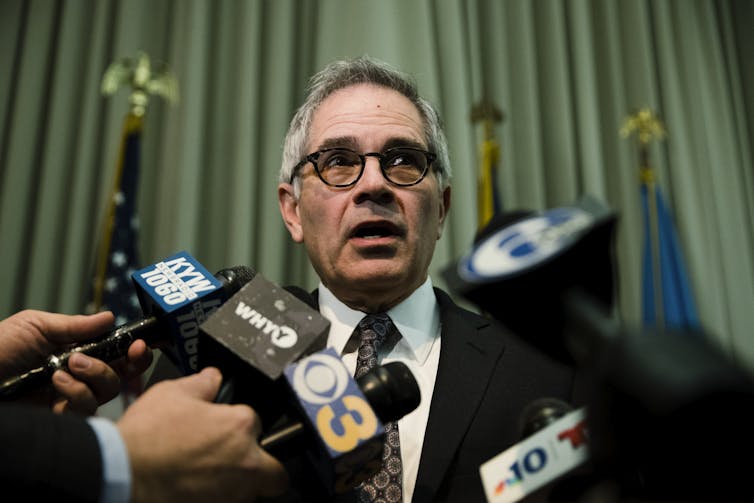 Philadelphia District Attorney Larry Krasner has drawn the ire of President Trump.
AP Photo/Matt Rourke[29]
Philadelphia District Attorney Larry Krasner has drawn the ire of President Trump.
AP Photo/Matt Rourke[29]
The experience of Aramis Ayala, the state attorney for the 9th Judicial Circuit Court of Florida, is a classic example of the obstacles these new prosecutors can face. After being elected in 2016[30], she announced that she would no longer seek the death penalty for any defendants tried by her office. Florida Gov. Rick Scott responded by reassigning 24 aggravated murder cases[31] to another state attorney who was amenable to the death penalty.
Ayala sued to have the cases returned to her jurisdiction. She lost[32].
What changed?
Nonetheless, progressive prosecutors would have never attained power in the first place if their views didn’t resonate with voters.
Michelle Alexander’s 2010 book, “The New Jim Crow[33],” deserves some credit for changing the way activists thought about crime and punishment. Alexander cast mass incarceration as a civil rights crisis by showing that people didn’t simply end up in jail because they were bad people who made poor choices. Nor did prison populations explode simply because there were more crimes being committed. Instead, mass incarceration was closely intertwined with race, poverty and government policy.
Among civil rights activists, issues like affirmative action in higher education had been consuming a lot of time, energy and resources. Alexander’s book helped redirect attention to racialized mass incarceration as a main battlefront in U.S. race relations.
Since its formation in 2013, the Black Lives Matter movement has made criminal justice reform a centerpiece of their activism. In Los Angeles, for example, the local chapter has led weekly demonstrations for over two years[34] in front of the Hall of Justice. They’re protesting Los Angeles County District Attorney Jackie Lacey for failing to adequately address police misconduct.
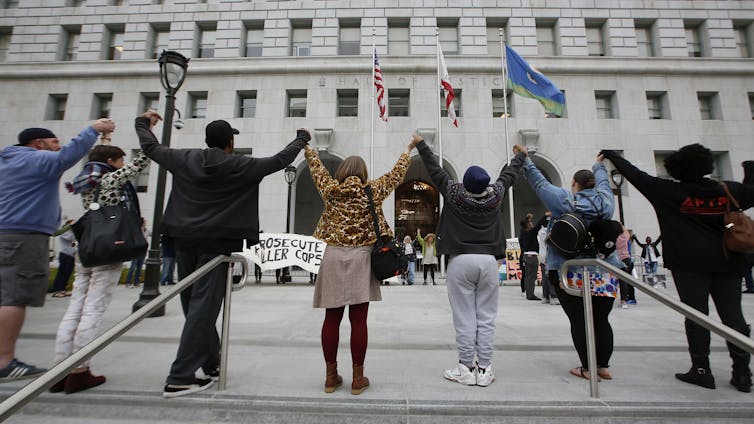 Protesters gather outside the Hall of Justice in Los Angeles in May 2018.
AP Photo/Damian Dovarganes[35]
Protesters gather outside the Hall of Justice in Los Angeles in May 2018.
AP Photo/Damian Dovarganes[35]
Lacey, who is up for reelection, faces two opponents. Both of them – former San Francisco District Attorney George Gascón and former public defender Rachel Rossi – are running on progressive platforms.
In March, we’ll see if the Los Angeles County District Attorney’s office – the nation’s largest county-wide prosecutorial agency – will be the latest to join the progressive prosecutor movement.
[ Deep knowledge, daily. Sign up for The Conversation’s newsletter[36]. ]
References
- ^ attacks from the left (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ to witness the execution of a mentally disabled man (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ of more than 50 law enforcement groups (www.theatlantic.com)
- ^ a landslide victory (ballotpedia.org)
- ^ vindicated by the 6th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals (casetext.com)
- ^ a lawyer and law professor (gould.usc.edu)
- ^ the prison population exploded (www.sentencingproject.org)
- ^ in order to force defendants into plea deals (www.hrw.org)
- ^ was able to show (www.google.com)
- ^ steadily declining in the 1990s and 2000s (qz.com)
- ^ one key statistic (qz.com)
- ^ roughly doubled (bostonreview.net)
- ^ Current Affairs (images.currentaffairs.org)
- ^ prosecutors had been the main drivers (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ prison population (www.sentencingproject.org)
- ^ nearly six times (www.pewresearch.org)
- ^ seemed to bolster the political careers of district attorneys (www.thedailybeast.com)
- ^ Larry Krasner (www.phillymag.com)
- ^ Rachael Rollins (theintercept.com)
- ^ Satana Deberry (www.heraldsun.com)
- ^ Parisa Dehghani-Tafti (www.huffpost.com)
- ^ Satana Deberry (d1n0c1ufntxbvh.cloudfront.net)
- ^ campaigned on (krasnerforda.com)
- ^ nearly 75% of the vote (ballotpedia.org)
- ^ told my law students (www.youtube.com)
- ^ hurt people hurt people (www.sciencedirect.com)
- ^ according to U.S. Attorney General William Barr (www.latimes.com)
- ^ singled out Krasner (www.phillyvoice.com)
- ^ AP Photo/Matt Rourke (www.apimages.com)
- ^ elected in 2016 (www.orlandosentinel.com)
- ^ responded by reassigning 24 aggravated murder cases (theintercept.com)
- ^ She lost (www.npr.org)
- ^ The New Jim Crow (books.google.com)
- ^ has led weekly demonstrations for over two years (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ AP Photo/Damian Dovarganes (www.apimages.com)
- ^ Sign up for The Conversation’s newsletter (theconversation.com)
Authors: Jody D. Armour, Roy P. Crocker Professor of Law, University of Southern California
Read more http://theconversation.com/how-being-tough-on-crime-became-a-political-liability-128515

