El Niño is back – that's good news or bad news, depending on where you live
- Written by Bob Leamon, Associate Research Scientist, University of Maryland, Baltimore County
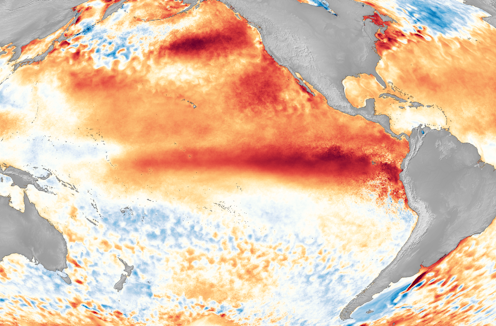
El Niño is officially here[1], and while it’s still weak right now, federal forecasters expect this global disrupter of worldwide weather patterns to gradually strengthen.
That may sound ominous, but El Niño – Spanish for “the little boy” – is not malevolent, or even automatically bad.
Here’s what forecasters expect, and what it means for the U.S.
What is El Niño?
El Niño is a climate pattern that starts with warm water building up in the tropical Pacific west of South America. This happens every three to seven years or so. It might last a few months or a couple of years[2].
Normally, the trade winds push warm water away from the coast there, allowing cooler water to surface[3]. But when the trade winds weaken[4], water near the equator can heat up, and that can have all kinds of effects through what are known as teleconnections. The ocean is so vast – covering approximately one-third of the planet, or about 15 times the size of the U.S. – that those sloshings of warm water have knock-on effects around the globe.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration explains teleconnections and the impact of El Niño.That warming at the equator during El Niño leads to the warming of the stratosphere, starting about 6.2 miles (10 kilometers) above the surface. Scientists are still studying how exactly this teleconnection occurs.
At the same time, the lower tropical stratosphere cools.
That combination can shift the upper-level winds known as the jet stream, which blow from west to east. Altering the jet stream can affect all kinds of weather variables, from temperatures to storms and winds that can tear hurricanes apart[5].
Basically, what happens in the Pacific doesn’t stay in the Pacific.
So, what does all that mean for you and me?
With apologies to Charles Dickens, El Niño tends to create a tale of two regions: the best of times for some, and the worst of times for others.
On average, El Niño years are warmer globally[6] than La Niña years – El Niño’s opposite. Globally, a strong El Niño can boost temperatures by about 0.7 degrees Fahrenheit (0.4 Celsius). But in North America, there is a lot of local variation.
El Niño years tend to be warmer across the northern part of the U.S. and in Canada, and the Pacific Northwest and Ohio Valley are often drier than usual in the winter and fall. The Southwest, on the other hand, tends to be cooler and wetter than average[7].
El Niño typically shifts the jet stream farther south, so it blows pretty much due west to east over the southern U.S. That shift tends to block moisture from the Gulf of Mexico, reducing the fuel for thunderstorms in the Southeast. La Niña, conversely, is associated with a more wavy and northward-shifted jet stream, which can enhance severe weather activity in the South and Southeast.
El Niño also affects hurricanes, but in different ways in the Atlantic and Pacific[9].
Over the Atlantic, El Niño tends to increase wind shear[10] – the change in wind speed with height in the atmosphere – which can tear apart hurricanes. But El Niño has the opposite effect in the eastern Pacific, where it can mean more storms. The ocean heat can also raise the risk of marine heat waves[11] that can devastate corals and ecosystems fish rely on.
In the middle of the U.S., El Niño is generally associated with warmer and drier conditions that can mildly increase the chances of a bountiful corn crop[12].
In contrast, El Niño can wreak havoc on crops in Southern Africa[13] and Australia[14] and increase Australia’s fire risk[15] with dangerously dry conditions. Brazil and northern South America also tend to be drier, while parts of Argentina and Chile tend to be wetter[16].
Of course, just because this is normally what happens doesn’t mean it happens every time. Witness California’s record rainfalls from multiple atmospheric rivers[18] at the end of the last La Niña, which normally would mean dry conditions.
Every weather event is somewhat different, so the influence of El Niño is a matter of probability, not certainty. How El Niño and La Niña will be influenced over time by climate change[19] isn’t yet clear.
The forecasts don’t all agree
Is 2023 going to be a record-breaking year? That’s the multibillion-dollar[20] question.
The National Weather Service declares the onset of El Niño when water temperatures are at least 0.9 F (0.5 C) above normal for a three-month period in what’s known as the Niño3.4 region[21]. That’s a large imaginary rectangle south of Hawaii along the equator.
For a strong El Niño, the Niño3.4 region needs to warm by 2.7 F (1.5 C) for three months. It’s not clear as of right now whether this El Niño will meet that threshold this year.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s first El Niño advisory of the year, released on June 8, sees an 84% chance of El Niño being greater than moderate by winter and a 56% chance that it will be strong.
Those forecasts can change, though, and different forecasting methods[23] offer different forecasts of the magnitude[24].
“Dynamical” models, similar to the models used for typical weather forecasts, have projected a very strong El Niño, whereas “static” or statistical models are far less optimistic. Personally, I’m a statistical modeler[25], and my own model doesn’t suggest a strong El Niño in 2023. Rather, my model – like other static models – predicts that 2023 will fizzle out, and after a couple of quiet, or neutral, years, we will see a strong El Niño in 2026. I did get the recent unusual “triple dip” La Niña[26] right, but I’m willing to be proved wrong by observations, as any good scientist should be.
But no computer model of any flavor has had experience with the globally super-high ocean temperatures that are occurring right now. The Atlantic is unusually warm[28], and that could offset some of the usual forces that come with El Niño.
References
- ^ officially here (www.climate.gov)
- ^ a few months or a couple of years (images.theconversation.com)
- ^ cooler water to surface (earthobservatory.nasa.gov)
- ^ when the trade winds weaken (oceanservice.noaa.gov)
- ^ tear hurricanes apart (theconversation.com)
- ^ El Niño years are warmer globally (public.wmo.int)
- ^ cooler and wetter than average (oceanservice.noaa.gov)
- ^ NOAA (www.climate.gov)
- ^ different ways in the Atlantic and Pacific (theconversation.com)
- ^ increase wind shear (theconversation.com)
- ^ risk of marine heat waves (theconversation.com)
- ^ chances of a bountiful corn crop (www.agweb.com)
- ^ on crops in Southern Africa (doi.org)
- ^ Australia (theconversation.com)
- ^ increase Australia’s fire risk (www.bom.gov.au)
- ^ Argentina and Chile tend to be wetter (earthobservatory.nasa.gov)
- ^ Ian Waldie/Getty Images (www.gettyimages.com)
- ^ multiple atmospheric rivers (www.nesdis.noaa.gov)
- ^ influenced over time by climate change (doi.org)
- ^ multibillion-dollar (www.ncei.noaa.gov)
- ^ Niño3.4 region (svs.gsfc.nasa.gov)
- ^ NOAA Climate.gov (www.climate.gov)
- ^ different forecasting methods (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ different forecasts of the magnitude (twitter.com)
- ^ I’m a statistical modeler (science.gsfc.nasa.gov)
- ^ “triple dip” La Niña (earthobservatory.nasa.gov)
- ^ Watchara Phomicinda/MediaNews Group/The Press-Enterprise via Getty Images (www.gettyimages.com)
- ^ is unusually warm (theconversation.com)
Authors: Bob Leamon, Associate Research Scientist, University of Maryland, Baltimore County

