What is a heat dome? An atmospheric scientist explains the weather phenomenon baking large parts of the country
- Written by William Gallus, Professor of Atmospheric Science, Iowa State University
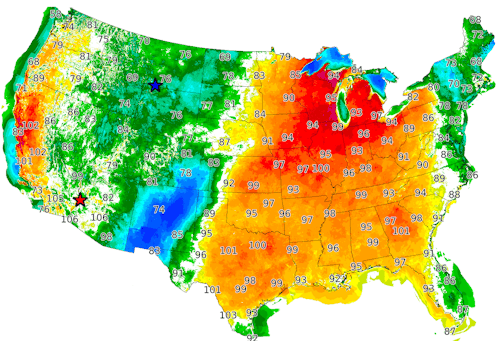
A heat dome occurs when a persistent region of high pressure traps heat over an area. The heat dome can stretch over several states and linger for days to weeks, leaving the people, crops and animals below to suffer through stagnant, hot air that can feel like an oven.
Typically, heat domes are tied to the behavior of the jet stream[1], a band of fast winds high in the atmosphere that generally runs west to east.
Normally, the jet stream has a wavelike pattern, meandering[2] north and then south and then north again. When these meanders in the jet stream become bigger, they move slower and can become stationary. That’s when heat domes can occur.
When the jet stream swings far to the north, air piles up and sinks. The air warms as it sinks[3], and the sinking air also keeps skies clear since it lowers humidity. That allows the sun to create hotter and hotter conditions near the ground.
If the air near the ground passes over mountains and descends, it can warm even more[4]. This downslope warming played a large role in the extremely hot temperatures in the Pacific Northwest during a heat dome event in 2021[5], when Washington set a state record with 120 degrees Fahrenheit (49 Celsius), and temperatures reached 121 F in British Columbia in Canada, surpassing the previous Canadian record by 8 degrees F (4 C).
Heat domes normally persist for several days in any one location, but they can last longer. They can also move, influencing neighboring areas over a week or two. The heat dome involved in the June 2022 U.S. heat wave crept eastward over time.
On rare occasions, the heat dome can be more persistent. That happened in the southern Plains in 1980[7], when as many as 10,000 people died during weeks of high summer heat. It also happened over much of the United States during the Dust Bowl years[8] of the 1930s.
A heat dome can have serious impacts on people, because the stagnant weather pattern that allows it to exist usually results in weak winds and an increase in humidity. Both factors make the heat feel worse – and become more dangerous[9] – because the human body is not cooled as much by sweating.
The heat index[10], a combination of heat and humidity, is often used to convey this danger by indicating what the temperature will feel like to most people. The high humidity also reduces the amount of cooling at night. Warm nights can leave people without air conditioners unable to cool off, which increases the risk of heat illnesses and deaths. With global warming, temperatures are already higher[11], too.
One of the worst recent examples of the impacts from a heat dome with high temperatures and humidity in the U.S. occurred in the summer of 1995[12], when an estimated 739 people died in the Chicago area[13] over five days.
References
- ^ the jet stream (www.youtube.com)
- ^ wavelike pattern, meandering (www.weather.gov)
- ^ air warms as it sinks (glossary.ametsoc.org)
- ^ warm even more (blog.weather.us)
- ^ heat dome event in 2021 (en.wikipedia.org)
- ^ NOAA (oceanservice.noaa.gov)
- ^ southern Plains in 1980 (www.hsdl.org)
- ^ during the Dust Bowl years (doi.org)
- ^ and become more dangerous (theconversation.com)
- ^ heat index (www.weather.gov)
- ^ temperatures are already higher (www.climate.gov)
- ^ in the summer of 1995 (www.weather.gov)
- ^ 739 people died in the Chicago area (www.chicagomag.com)
Authors: William Gallus, Professor of Atmospheric Science, Iowa State University

