The US military presence in Europe has been declining for 30 years – the current crisis in Ukraine may reverse that trend
- Written by Michael A. Allen, Associate Professor of Political Science, Boise State University
Up to 8,500 U.S. troops could soon be heading to Eastern Europe[1] – bolstering an American military presence in the continent that has been in decline since the end of the Cold War.
News of the possible deployment, announced on Jan. 24, 2022, by the Pentagon, comes as Russia and the United States continue to maneuver in the face of an escalating crisis in Ukraine.
We are a team of researchers who study U.S. troop deployments and how they affect the security[2], perceptions[3], economy, social sphere[4] and environment[5] of host countries. Understanding the changing U.S. military commitment to European countries helps us understand what is at stake in Europe and U.S. credibility in the region.
President Joe Biden signaled during a press conference[6] on Jan. 19 that the U.S. would increase its troop presence in NATO countries in Eastern Europe if Russia invades Ukraine as it seems poised to do. Just days later, he directed Secretary of Defense Lloyd Austin to place thousands of U.S. troops on heightened alert for deployment to Eastern Europe.
The decision was framed by the Pentagon as the U.S. carrying through with its obligations to protect the security of NATO allies.
While Biden acknowledges that Ukraine is not a member of NATO, he emphasized that neighboring countries Poland and Romania are[7], and that the U.S. has an obligation to protect them. A large troop deployment[8] – potentially to bolster NATO’s existing presence in those two countries – would meet that obligation.
The U.S. and Russia have historically been cautious in not placing troops in places that would be considered a provocation. They generally avoid each other’s sphere of influence[9], even when responding to the other’s deployments. Yet the NATO allies in Eastern Europe, many of which were once Soviet satellite states, provide a gray area that both the U.S. and Russia may view as within their own sphere of influence.
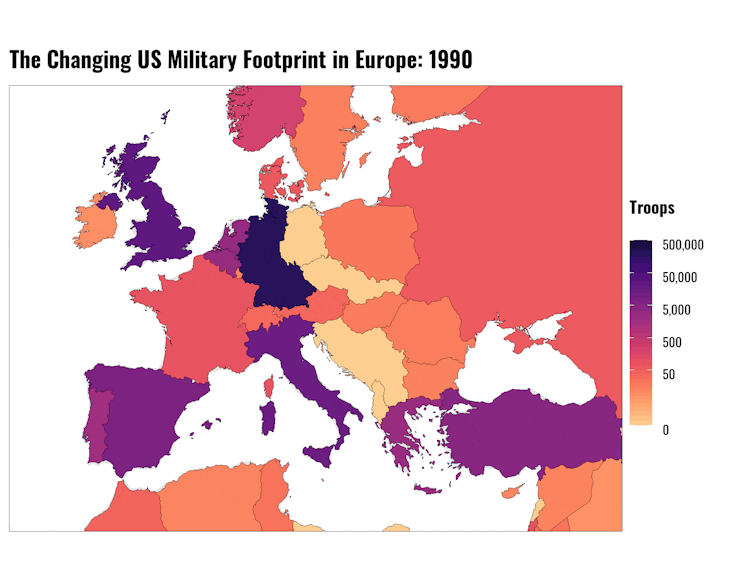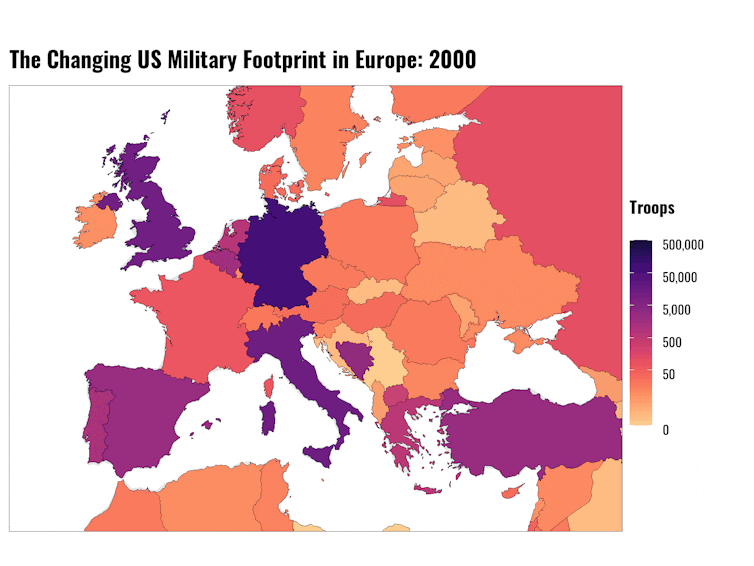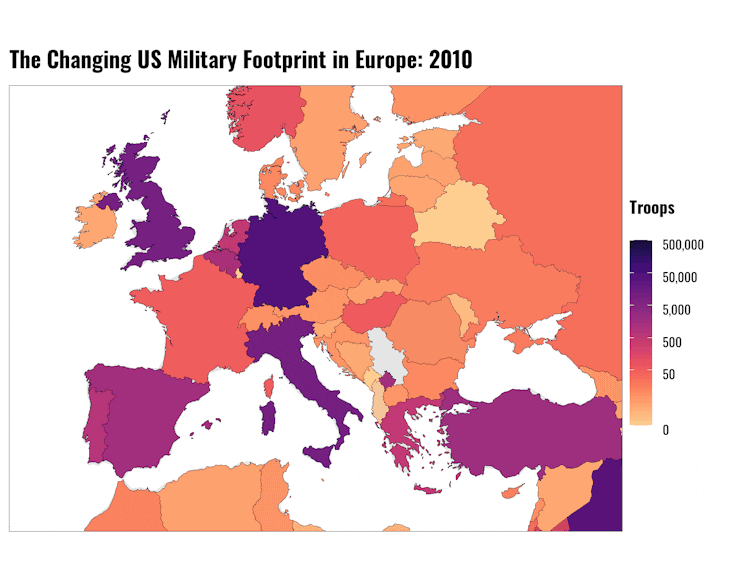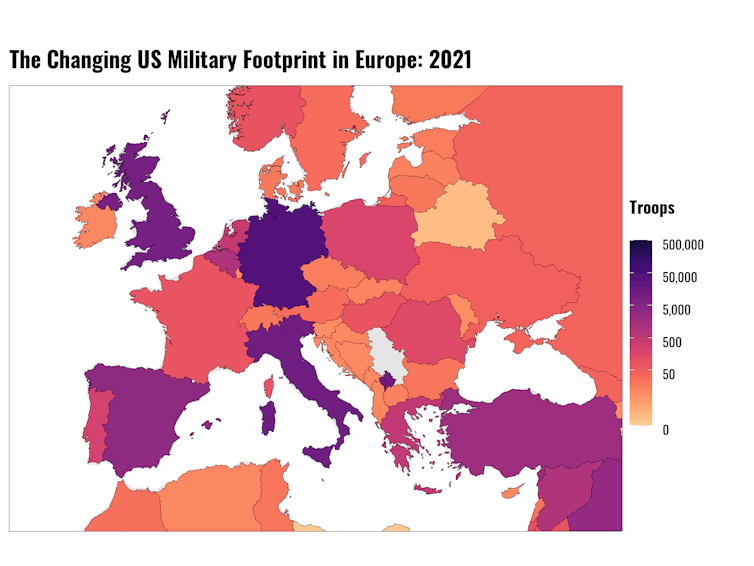
The US military’s history in Europe
Since the end of World War II, the United States has deployed hundreds of thousands of service members[10] to Europe. These deployments were vital in not only stabilizing Western Europe following the war, but also in exerting U.S. influence in the postwar environment.
Interactions between the U.S. and European countries during this period involved the creation of a series of institutions to help structure the rules and norms of international relations. These organizations have persisted in part because the United States provides security commitments to countries that accept and promote them. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization[11] (NATO), a military alliance established in 1949 as a bulwark to Soviet expansionism, was central to these efforts.
At its height in the late 1950s, U.S. presence in Europe consisted of about 430,000 troops, stationed in places like West Germany and the U.K.
After the end of the Cold War, NATO sought to redefine its mission from one that checked Russian aggression to European stability more generally[12]. This change in mission came with the expansion of NATO membership to Central and Eastern European countries, such as Hungary and Poland, and the Baltic States of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. With NATO membership came new deployments of U.S. service members to these countries.
NATO has also sought to expand its relationships with non-member states throughout Eastern and Central Europe through the Membership Action Plan[13], which provides advice and assistance to countries wishing to join NATO.
This eastward push came with objections from Russia in the 1990s[14], which has long worried about the security of its western borders with Europe. Russia’s concern about NATO expanding to its border continues today, as seen in President Vladimir Putin’s demand[15] that NATO forces pull back from deploying in former Soviet states.
A shift away from Europe?
If the U.S. follows through with beefing up its military presence in Eastern Europe, it would reverse a trend that has seen American troop numbers dwindle in Europe significantly since the end of the Cold War.
The Sept. 11, 2001, attacks in particular marked a dramatic shift in where the U.S. focused its troop deployments and security concerns. The beginning of the war in Afghanistan in 2001 and the 2003 invasion of Iraq brought massive changes in the United States’ military position globally as it shifted focus to Central Asia and the Middle East.
In 1989, the United States had 248,621 permanent troops stationed[16] in West Germany, 27,639 in the United Kingdom, 15,706 in Italy and 3,382 in Greece. By September 2021, U.S. troop numbers had fallen to 35,457 in Germany, 9,563 in the United Kingdom, 12,434 in Italy and 429 in Greece.
While the size of U.S. deployments to Europe have declined dramatically since their Cold War heights, they are still very large relative to most other U.S. deployments.
Without the threat of the Soviet Union, though, public opposition[17] to foreign deployments has also increased[18] in the post-Cold War era.
However, rising tensions with Russia have in the recent past prompted U.S. presidents to dedicate additional military aid and deployments to Poland and the Baltic States[19].
This trend looks set to continue if the Pentagon does indeed deploy thousands of troops to Eastern Europe in the face of a threatened invasion by Russia of Ukraine.
[Get the best of The Conversation, every weekend. Sign up for our weekly newsletter[20].]
References
- ^ soon be heading to Eastern Europe (www.cnn.com)
- ^ security (theconversation.com)
- ^ perceptions (www.cambridge.org)
- ^ social sphere (theconversation.com)
- ^ environment (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ signaled during a press conference (youtu.be)
- ^ Poland and Romania are (www.nato.int)
- ^ large troop deployment (tnsr.org)
- ^ avoid each other’s sphere of influence (www.journals.uchicago.edu)
- ^ hundreds of thousands of service members (theconversation.com)
- ^ North Atlantic Treaty Organization (www.nato.int)
- ^ NATO sought to redefine its mission from one that checked Russian aggression to European stability more generally (www.nato.int)
- ^ Membership Action Plan (www.nato.int)
- ^ objections from Russia in the 1990s (transatlanticrelations.org)
- ^ President Vladimir Putin’s demand (www.aljazeera.com)
- ^ United States had 248,621 permanent troops stationed (journals.sagepub.com)
- ^ public opposition (www.pewresearch.org)
- ^ increased (www.pewresearch.org)
- ^ additional military aid and deployments to Poland and the Baltic States (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ Sign up for our weekly newsletter (memberservices.theconversation.com)
Authors: Michael A. Allen, Associate Professor of Political Science, Boise State University

