How to hide from a drone – the subtle art of 'ghosting' in the age of surveillance
- Written by Austin Choi-Fitzpatrick, Associate Professor of Political Sociology, University of San Diego
Drones of all sizes are being used by environmental advocates to monitor deforestation, by conservationists to track poachers, and by journalists and activists to document large protests. As a political sociologist[1] who studies social movements and drones, I document a wide range of nonviolent and pro-social drone uses in my new book, “The Good Drone[2].” I show that these efforts have the potential to democratize surveillance.
But when the Department of Homeland Security redirects large, fixed-wing drones from the U.S.-Mexico border to monitor protests[3], and when towns experiment with using drones to test people for fevers[4], it’s time to think about how many eyes are in the sky and how to avoid unwanted aerial surveillance. One way that’s within reach of nearly everyone is learning how to simply disappear from view.
Crowded skies
Over the past decade there’s been an explosion in the public’s use of drones – everyday people with everyday tech doing interesting things[5]. As drones enter already-crowded airspace, the Federal Aviation Administration is struggling to respond[6]. The near future is likely to see even more of these devices in the sky, flown by an ever-growing cast of social, political and economic actors.
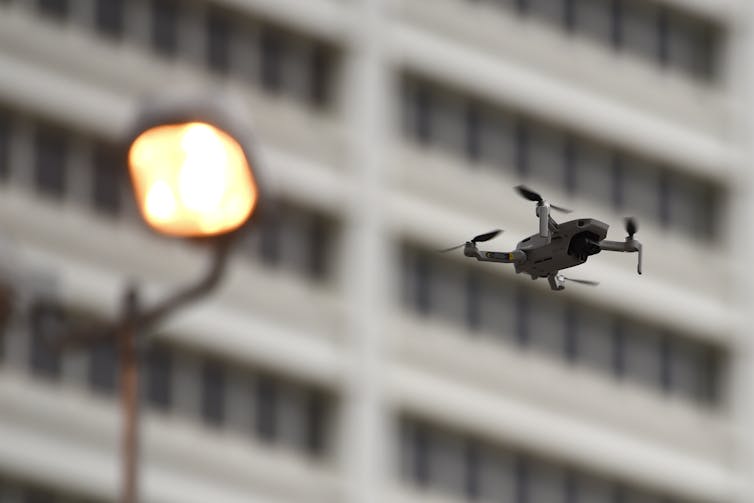 A law enforcement drone flew over demonstrators, Friday, June 5, 2020, in Atlanta.
AP Photo/Mike Stewart[7]
A law enforcement drone flew over demonstrators, Friday, June 5, 2020, in Atlanta.
AP Photo/Mike Stewart[7]
Public opinion about the use and spread of drones is still up in the air[8], but burgeoning drone use has sparked numerous efforts to curtail drones. These responses range from public policies exerting community control over local airspace, to the development of sophisticated jamming equipment and tactics for knocking drones out of the sky.
From startups to major defense contractors, there is a scramble to deny airspace to drones, to hijack drones digitally, to control drones physically and to shoot drones down. Anti-drone measures range from simple blunt force, 10-gauge shotguns[9], to the poetic: well-trained hawks[10].
Many of these anti-drone measures are expensive and complicated. Some are illegal. The most affordable – and legal – way to avoid drone technology is hiding[11].
How to disappear
The first thing you can do to hide from a drone is to take advantage of the natural and built environment. It’s possible to wait for bad weather, since smaller devices like those used by local police have a hard time flying in high winds, dense fogs and heavy rains.
Trees, walls, alcoves and tunnels are more reliable than the weather, and they offer shelter from the high-flying drones used by the Department of Homeland Security.
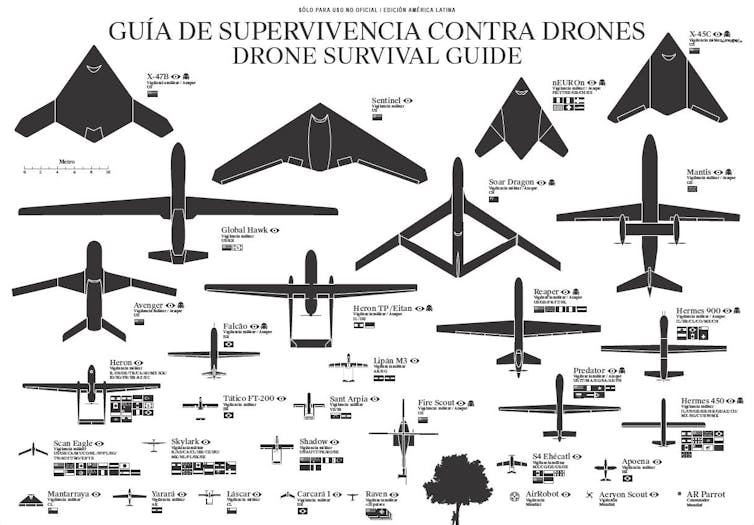 In some parts of the world, hiding from drones is a matter of life and death.
Drone Survival Guide, CC BY-NC[12][13]
In some parts of the world, hiding from drones is a matter of life and death.
Drone Survival Guide, CC BY-NC[12][13]
The second thing you can do is minimize your digital footprints. It’s smart to avoid using wireless devices like mobile phones or GPS systems, since they have digital signatures that can reveal your location. This is useful for evading drones, but is also important for avoiding other privacy-invading technologies.
The third thing you can do is confuse a drone. Placing mirrors on the ground, standing over broken glass, and wearing elaborate headgear, machine-readable blankets[14] or sensor-jamming jackets[15] can break up and distort the image a drone sees.
Mannequins and other forms of mimicry can confuse both on-board sensors and the analysts charged with monitoring the drone’s video and sensor feeds.
Drones equipped with infrared sensors will see right through the mannequin trick, but are confused by tactics that mask the body’s temperature. For example, a space blanket will mask significant amounts of the body’s heat, as will simply hiding in an area that matches the body’s temperature, like a building or sidewalk exhaust vent.
The fourth, and most practical, thing you can do to protect yourself from drone surveillance is to get a disguise. The growth of mass surveillance has led to an explosion in creative experiments meant to mask one’s identity. But some of the smartest ideas are decidedly old-school and low-tech. Clothing is the first choice, because hats, glasses, masks and scarves go a long way toward scrambling drone-based facial-recognition software.
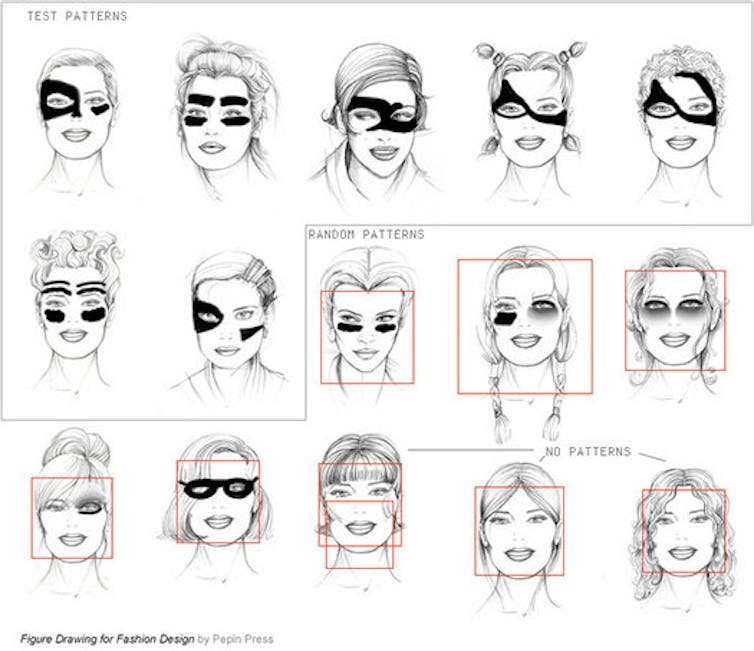 Clever use of makeup can thwart facial recognition systems.
John C Bullas BSc MSc PhD MCIHT MIAT/Flickr, CC BY-NC-ND[16][17]
Clever use of makeup can thwart facial recognition systems.
John C Bullas BSc MSc PhD MCIHT MIAT/Flickr, CC BY-NC-ND[16][17]
Your gait is as unique as your fingerprint. As gait-recognition software evolves, it will be important to also mask the key pivot points used in identifying the walker. It may be that the best response is affecting a limp, using a minor leg brace or wearing extremely loose clothing.
Artists and scientists have taken these approaches a step further, developing a hoodie wrap[18] that’s intended to shield the owner’s heat signature and to scramble facial recognition software, and glasses[19] intended to foil facial recognition systems.
Keep an umbrella handy
These innovations are alluring, but umbrellas may prove to be the most ubiquitous and robust tactic in this list. They’re affordable, easy to carry, hard to see around and can be disposed of in a hurry. Plus you can build a high-tech one[20], if you want.
Sign up for The Conversation’s newsletter[21].]
It would be nice to live in a world with fewer impositions on privacy, one in which law enforcement did not use small quadcopters and the Department of Homeland Security did not redeploy large Predator drones to surveil protesters. And, for people in some parts of the world, it would be nice not to associate the sound of a drone with impending missile fire. But given that those eyes are in the sky, it’s good to know how to hide.

References
- ^ political sociologist (scholar.google.com)
- ^ The Good Drone (mitpress.mit.edu)
- ^ monitor protests (www.nytimes.com)
- ^ test people for fevers (www.nbcnews.com)
- ^ interesting things (digital.sandiego.edu)
- ^ struggling to respond (doi.org)
- ^ AP Photo/Mike Stewart (www.apimages.com)
- ^ up in the air (theconversation.com)
- ^ 10-gauge shotguns (www.popularmechanics.com)
- ^ well-trained hawks (www.washingtonpost.com)
- ^ hiding (www.dronesurvivalguide.org)
- ^ Drone Survival Guide (www.dronesurvivalguide.org)
- ^ CC BY-NC (creativecommons.org)
- ^ machine-readable blankets (www.theguardian.com)
- ^ sensor-jamming jackets (projectkovr.com)
- ^ John C Bullas BSc MSc PhD MCIHT MIAT/Flickr (www.flickr.com)
- ^ CC BY-NC-ND (creativecommons.org)
- ^ hoodie wrap (weburbanist.com)
- ^ glasses (www.chicagotribune.com)
- ^ high-tech one (survival.sentientcity.net)
- ^ Sign up for The Conversation’s newsletter (theconversation.com)
Authors: Austin Choi-Fitzpatrick, Associate Professor of Political Sociology, University of San Diego

